108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-4792 调节五倍子黄酮以抑制 A549 细胞增殖、侵袭和诱导细胞凋亡的生物信息学分析
Authors Liu P, Pu J, Zhang J, Chen Z, Wei K, Shi L
Received 3 August 2018
Accepted for publication 27 December 2018
Published 20 February 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1401—1412
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S182525
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
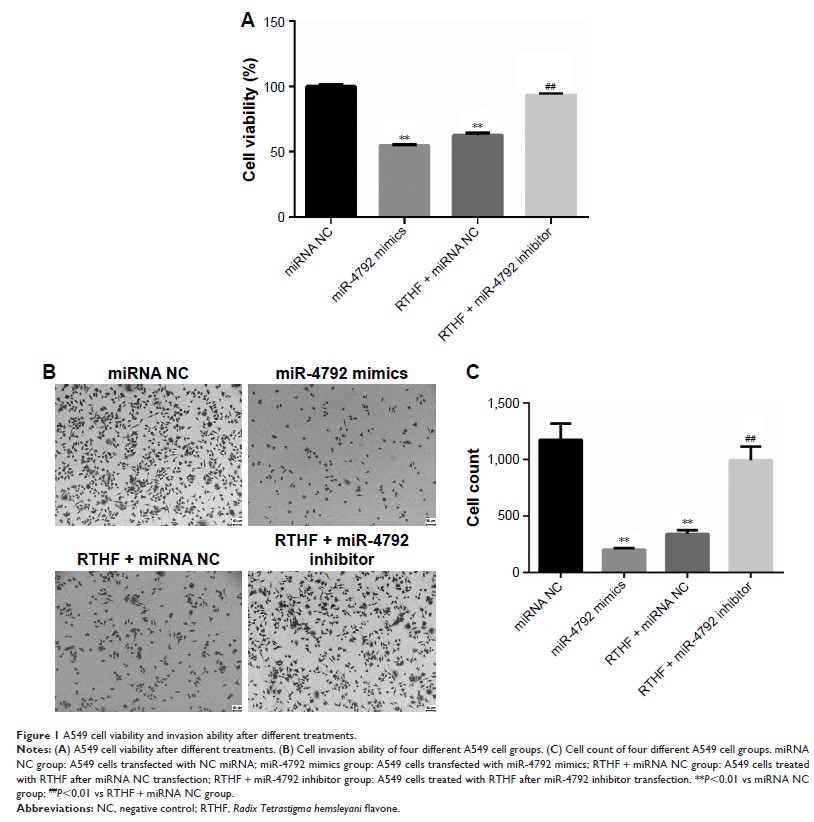
Background: Radix Tetrastigma hemsleyani ,
a kind of Chinese medicinal herb, contains multiple medicinal ingredients and
can exert a variety of pharmacological activities. Our previous study revealed
that miR-4792 was significantly upregulated in Radix Tetrastigma hemsleyani flavone
(RTHF)-treated A549 cells; however, the regulatory mechanism of RTHF-treated
A549 cells remains unclear.
Materials and methods: In this
study, we investigated the antitumor mechanism and regulatory pathway of
miR-4792 in RTHF-treated A549 cells, and the target genes were predicted and
pathway enrichment of miR-4792 was performed using bioinformatic analysis.
Results: Our
results confirmed that the upregulated expression of miR-4792 could inhibit
cell proliferation and invasion, provoke cell cycle arrest, and induce
apoptosis in A549 cells. Gene Ontology analysis showed that target genes of
miR-4792 were enriched in protein binding, cytosol, cytoplasm, plasma membrane,
and metal ion binding. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis showed
that target genes of miR-4792 were enriched in aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis,
AGE–RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications, sphingolipid signaling
pathway, neuroactive ligand–receptor interaction, glycosaminoglycan
degradation, and regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes. Additionally, FOXC1 was
identified as an important target gene of miR-4792 in RTHF-treated A549 cells,
and miR-4792 may be the target of some apoptotic-related proteins involved in
induction of apoptosis in A549 cells by RTHF. Moreover, the intracellular Ca2+ levels of
A549 cells were increased after RTHF treatment, which may be involved in the
anticancer regulatory process of miR-4792 in RTHF-treated A549 cells.
Conclusion: These
findings suggest a novel therapeutic approach for lung cancer that will be
investigated in future studies.
Keywords: Radix Tetrastigma hemsleyani ,
flavone, miR-4792, GO, KEGG, FOXC1, potential therapeutic agents