108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

细胞外基质蛋白 1(ECM1)与人膀胱癌的潜在致癌作用有关
Authors Wang Z, Zhou Q, Li A, Huang W, Cai Z, Chen W
Received 18 October 2018
Accepted for publication 18 January 2019
Published 20 February 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1423—1432
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S191321
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background: Bladder
cancer (BCa) is a common urological malignant tumor worldwide, and recurrence
and death still remain high. New therapeutic targets are needed to treat patients
who are not sensitive to current therapy. Extracellular matrix protein 1 (ECM1)
is a key player in multiple epithelial malignancies. However, the knowledge
regarding the expression of ECM1 in BCa and the mechanisms by which ECM1
affects BCa tumor progression is unclear.
Materials and methods: ECM1
expression levels in BCa tissues and cells were detected by quantitative
real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), immunohistochemistry and Western blot. ECM1 expression
was suppressed by shRNAs. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), luminescent cell
viability assay and 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU) assay were used to detect
cell proliferation. Flow cytometry and transwell assay were used to evaluate
cell apoptosis and invasion, respectively. All statistical analyses were
performed by using the GraphPad Prism 7 software package.
Results: In this
study, the expression of ECM1 in BCa specimens and cell lines was examined
and displayed a significant increase compared with noncancerous counterparts,
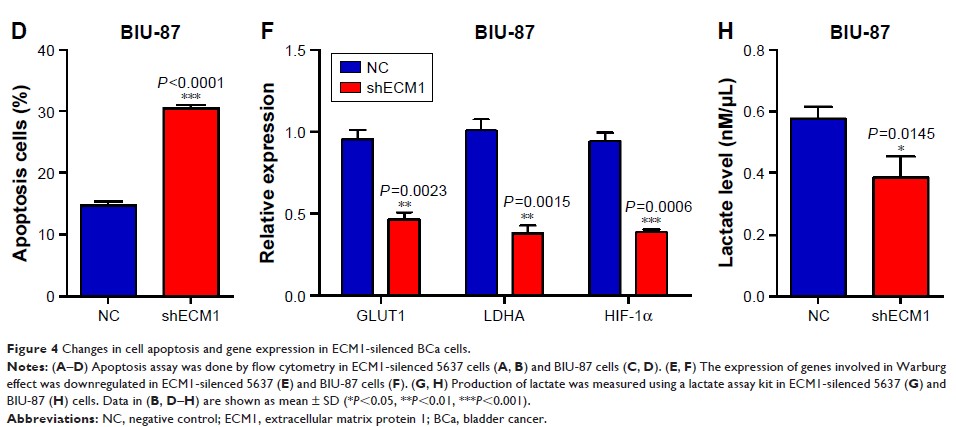
while ECM1 -knockdown
affected not only cell proliferation and migration, but also cell invasion
ability and apoptosis potential, corresponding to the finding that ECM1 overexpression
in BCa patients was associated with a poor prognosis. Additionally, after
suppression of ECM1 , the expression of glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1 ), lactate
dehydrogenase (LDHA )
and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α ), genes involved in Warburg effect regulation,
were significantly decreased, and the lactate production was also obviously
reduced in ECM1 -silenced
cells.
Conclusion: Our
investigations revealed that the expression of ECM1 was closely associated with
tumor cell growth, migration and apoptosis at least in part through regulation
of Warburg effect, defining ECM1 as an effective predictor in the
carcinogenesis and postoperative recurrence of human BCa.
Keywords: bladder
cancer, extracellular matrix protein 1, proliferation, migration, invasion