108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用紫杉醇纳米粒的慢性化疗在体外和体内诱导肺癌细胞凋亡
Authors Zhao X, Fan J, Wu P, Wei C, Chen Q, Ming Z, Yan J, Yang L
Received 19 September 2018
Accepted for publication 4 January 2019
Published 19 February 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 1299—1309
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S188049
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Aim: Paclitaxel
(PTX) is an effective antitumor drug. Previous research demonstrated that
paclitaxel nanoparticles (PTX-NPs) exhibited the greatest antitumor effect at
15 hours after light onset (15 HALO), but the mechanism in chronic chemotherapy
is still unknown. In our study, we investigated whether PTX-NPs regulated
Period2 (Per2) during chronic chemotherapy to induce apoptosis in vivo and in
vitro.
Methods: To
improve the antitumor effect and reduce organ damage induced by PTX treatment,
PTX-NPs were prepared using a film dispersion method. Then, A549 cells were
treated with PTX-NPs at 0, 5, 10, 15, and 20 HALO. An annexin/PI V-FITC
apoptosis kit was measured for apoptosis, and PI was analyzed for cell cycle.
The relative mechanism was detected by RT-PCR and Western blotting. Tumor
volume and weight were measured to evaluate the antitumor effect of the
PTX-NPs, and H&E staining was performed to assess organ damage.
Results: Cell
cycle analysis demonstrated that PTX-NPs blocked cell cycle in G2 phase and
that the ratio of cell death was significantly increased in A549 cells, while
the ratios of cells in G2 phase and of apoptotic cells were highest at 15 HALO.
Evaluation of in vivo antitumor activity revealed that PTX-NPs inhibited tumor
growth and decreased tumor weight at 15 HALO. RT-PCR and Western blotting
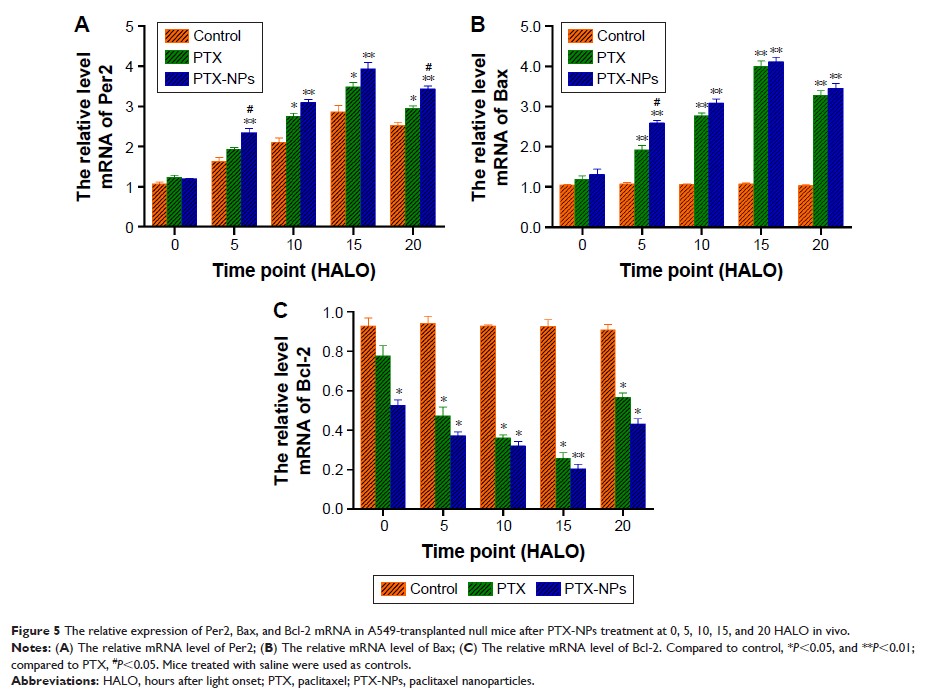
demonstrated that PTX-NPs upregulated Per2 mRNA and protein expression, and the
highest Per2 expression was observed at 15 HALO in vivo and in vitro.
Meanwhile, Bax mRNA and protein expression was upregulated, while Bcl-2 mRNA
and protein expression was downregulated after PTX-NPs treatment in vivo.
Moreover, H&E staining revealed that PTX-NPs reduced liver damage at 15
HALO.
Conclusion: PTX-NPs
exhibited the most effective antitumor activity and reduced liver damage at 15
HALO through upregulation of Per2 expression to induce apoptosis in vivo and in
vitro.
Keywords: paclitaxel
nanoparticles, chronic chemotherapy, Per2, apoptosis, lung cancer