108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CT 引导下冷冻消融治疗无法切除的盆腔复发性结直肠癌:一项回顾性研究
Authors Wang Y, He XH, Xu LC, Huang HZ, Li GD, Wang YH, Li WT, Wang GZ
Received 5 October 2018
Accepted for publication 27 January 2019
Published 19 February 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1379—1387
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S189897
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Arseniy Yuzhalin
Objective: The study
aimed to investigate the efficacy of computed tomography (CT)-guided
cryoablation debulking of unresectable pelvic recurrent colorectal cancer
(CRC).
Patients and methods: From
January 2013 to April 2016, 30 patients (18 males and 12 females; aged
57.8±10.5 years) with unresectable pelvic recurrent CRC who had previously
received radiotherapy or chemotherapy were included. A total of 35 tumors
ranging from 1.2 to 6.3 cm underwent cryoablation. Tumor response was evaluated
1 month after cryoablation according to the Modified Response Evaluation
Criteria in Solid Tumors. Logistic regression was used to analyze the risk
factors for tumor response. Degree of pain palliation was also determined using
the Numerical Rating Scale. Cox proportional hazard models were used to
identify predictors of outcomes.
Results: Cryoablation
was successfully performed in all patients. Complete response (CR) was achieved
for 27 tumors in 23 patients and partial response was achieved for eight tumors
in seven patients 1 month after cryoablation. The rate of CR was 77.14%, and
tumor size was an independent risk factor for CR. Pain relief was satisfactory
in 21 symptomatic patients (P <0.001), and the median duration of pain relief
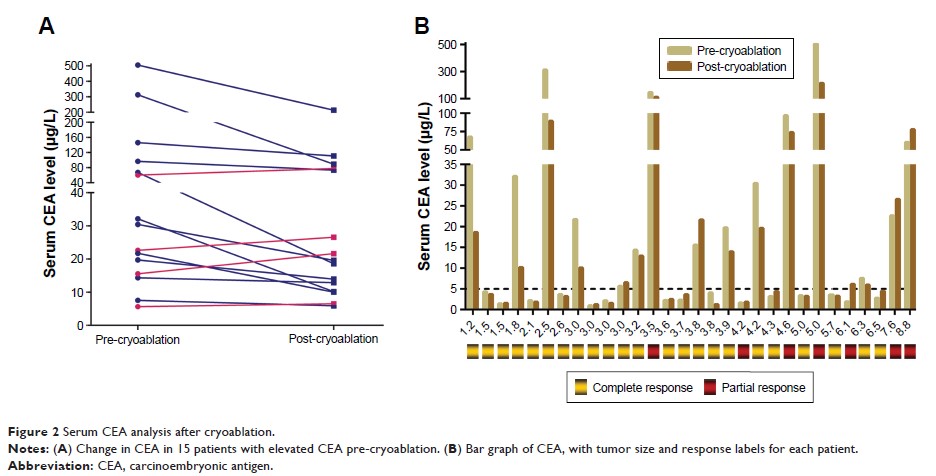
was 6.0 months (95% CI: 2.67–9.33). Serum carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) was
significantly decreased after cryoablation in 15 patients with elevated CEA (P =0.005). The
median progression-free survival (PFS) was 10.0 months (95% CI: 4.43–15.67).
Multivariate analysis revealed that tumor size (HR =3.089, P <0.001), sex
(HR =0.089, P =0.002), and elevated CEA (HR =7.015, P =0.002) were
independent predictors of PFS.
Conclusion: CT-guided
cryoablation is a safe and effective therapeutic option for pelvic recurrent
CRC. Tumor size is an important predictor of poor outcomes.
Keywords: cryoablation,
colorectal cancer, pelvic recurrence, pain, ablation