108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

布地奈德结合物的合成及其抗炎作用:一项初步研究
Authors Yan Y, Wang P, Li R, Sun Y, Zhang R, Huo C, Xing J, Dong Y
Received 26 October 2018
Accepted for publication 25 January 2019
Published 19 February 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 681—694
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S192348
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Georgios D. Panos
Purpose: Budesonide
(Bud) is a nonhalogenated glucocorticoid with high anti-inflammatory potency
and low systemic side effects. However, the poor water solubility of Bud
affects its dissolution and release behavior, thus influencing its
anti-inflammatory effect. This study was aimed at synthesizing and evaluating
novel conjugates of Bud, hoping to increase the anti-inflammatory activity of
Bud by improving its water solubility.
Materials and methods: Seven
novel Bud conjugates (3a–3g) were designed
and synthesized in this study. Besides, the equilibrium solubility, cell
viability, in vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activity, and the hydrolysis
behavior of the conjugates in different pH solutions, rat and human plasma, and
rat lung homogenate were studied in detail.
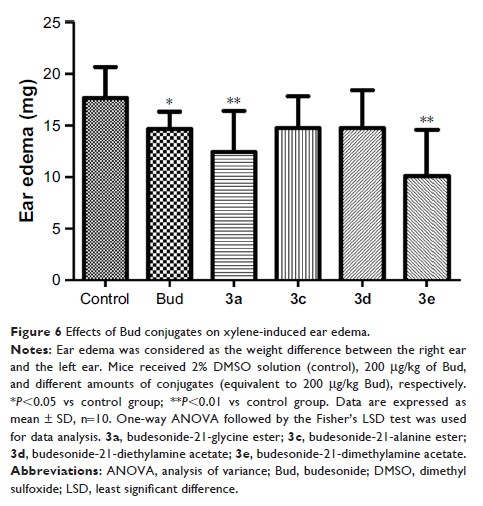
Results: As compared
to Bud, the equilibrium solubility of 3a, 3c, and 3e was
significantly increased; 3a, 3b, and 3c significantly
inhibited the interleukin-6 production in lipopolysaccharide-induced A549
cells; 3a and 3e could
significantly decrease the xylene-induced ear edema; and 3a and 3c were
gradually and slowly hydrolyzed into Bud in the alveolar fluid and lung
homogenate and broken down quickly in plasma.
Conclusion: The amino
acid ester compounds budesonide-21-glycine ester (3a) and
budesonide-21-alanine ester (3c) were selected
as potential conjugates of Bud. This study would provide a theoretical and an
experimental basis for the in vivo process of glucocorticoids and the treatment
of inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: budesonide,
glucocorticoid, anti-inflammatory effect, equilibrium solubility, hydrolysis behaviour