108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Forskolin 通过调节 Axin/β-catenin 信号通路在非霍奇金淋巴瘤中发挥抗癌作用
Received 19 July 2018
Accepted for publication 10 January 2019
Published 19 February 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1685—1696
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S180754
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Background: Non-Hodgkin’s
lymphomas (NHLs) account for 85% of lymphomas, which are characterized by
high-degree malignancy, rapid progress, and even invasion into central nervous
system in pediatric patients. Although the cure rate of pediatric NHL has
improved, some patients have still underwent recurrence or death. This study
focuses on the effects and mechanism of forskolin on the progression of NHL,
aiming to find efficient therapy methods for pediatric NHL.
Methods: MTT, flow
cytometry and mice tumor bearing experiments were used to evaluate the effects
of forskolin on NHL cell proliferation, apoptosis and tumorigenesis. Western
blotting and RT-PCR assays were used to detect protein and mRNA expression.
Immunohistochemistry technology was recruited to analyze Ki-67 expression in
tumor tissues.
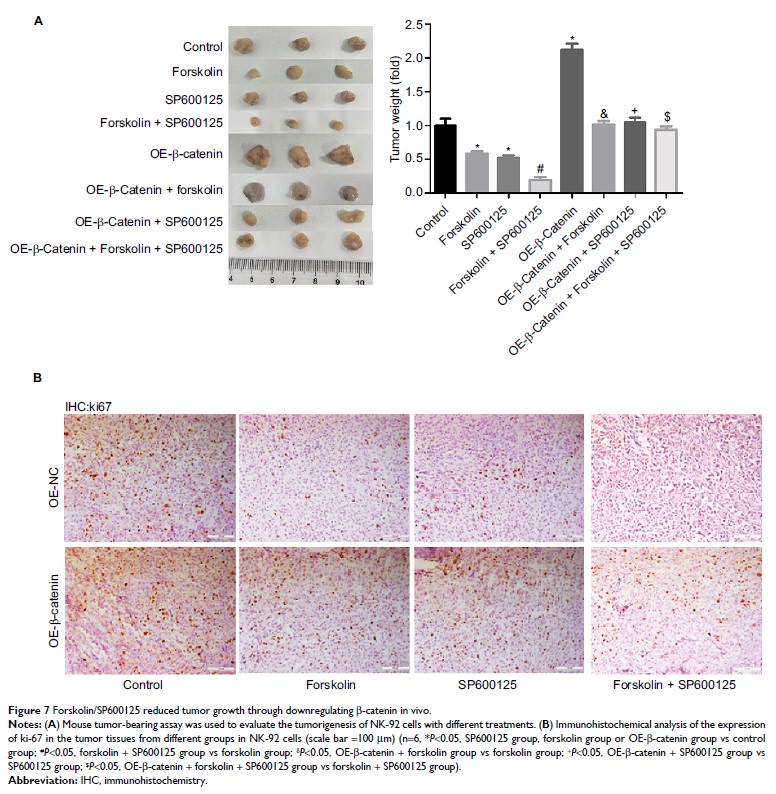
Results: Forskolin
significantly increased the expression of cleaved caspase-3/9 in both NHL
Toledo and NK-92 cell lines, and inhibited cell growth. Besides, forskolin
obviously reduced the expression of β-catenin protein, promoted its
ubiquitination, enhanced its transportation from nuclear to cytoplasm, as well
as decreased the expression of its downstream oncogenes c-myc and cyclin D1 through
upregulating Axin expression and stability and inhibiting Axin ubiquitination.
Moreover, forskolin enhanced the effects of SP600125, an inhibitor of c-Jun
N-terminal kinase signaling on cell apoptosis promotion and tumorigenesis
inhibition via Axin-induced β-catenin signaling repression.
Conclusion: The current
study clarifies that forskolin can inhibit the progression of NHL through
Axin-mediated inhibition of β-catenin signaling. Moreover, forskolin improves
the effects of SP600125 on cell apoptosis enhancement and tumorigenesis
inhibition of NHL cells. These findings provide theoretical foundation of
serving forskolin as a new effective therapeutic drug for pediatric NHL.
Keywords: forskolin,
SP600125, Axin, β-catenin, carcinogens