108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

上调 CKAP2L 表达可促进肺腺癌的侵袭,并且与预后不良有关
Authors Xiong GS, Li LY, Chen XB, Song SN, Zhao YP, Cai WK, Peng JP
Received 1 August 2018
Accepted for publication 19 December 2018
Published 12 February 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1171—1180
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S182242
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Aim: The
purpose of this study is to consider the function of cytoskeleton-associated
protein 2-like (CKAP2L) in lung adenocarcinoma (LAD) development and its
prognostic value.
Methods: The mRNA
expression of CKAP2L and its correlation with clinical factors in LAD patients
were analyzed from the data taken from The Cancer Genome Atlas and The First
Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University. We constructed H460 and A549
cell lines with silenced CKAP2L using RNA interference. Cell counting kit-8
assay and colony formation assays were carried out to determine the function of
CKAP2L in H460 and A549 cell proliferation. Transwell and wound healing assays
were applied to determine the effect of CKAP2L on H460 and A549 cell invasion
and migration. The influences of CKAP2L on mitogen-activated protein kinase
signaling pathway-related proteins were tested by Western blotting.
Results: CKAP2L
expression is enhanced in LAD tissues and is predictive of poor prognosis in
LAD patients. High expression of CKAP2L is associated with stage (P <0.001), lymph
node status (P =0.002),
and metastasis (P =0.025).
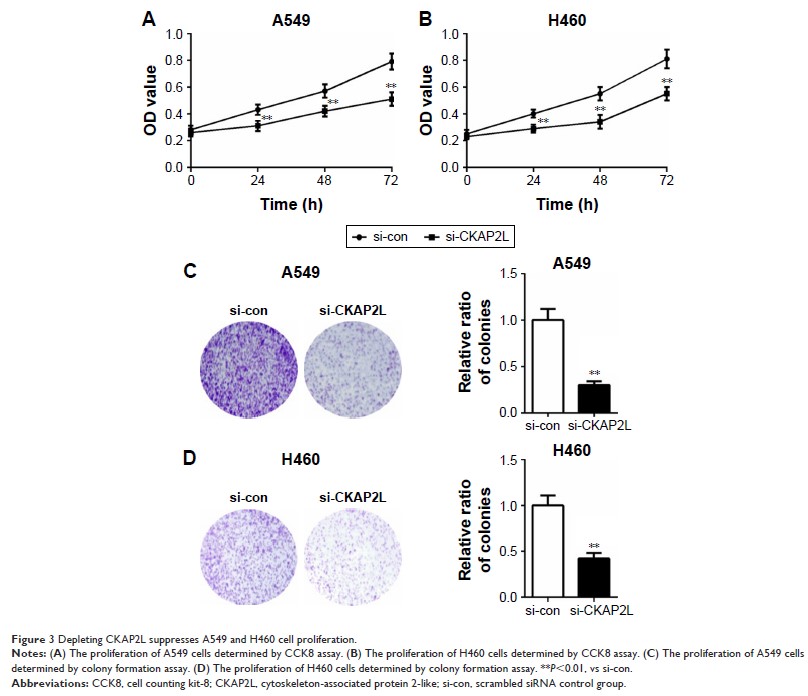
Depletion of CKAP2L dramatically suppressed the proliferation, migration, and
invasion of H460 and A549 cells. Moreover, the ratio of p-MEK/MEK and p-ERK/ERK
reduced obviously in A549 cells after depleting CKAP2L.
Conclusion: Our
findings implied that CKAP2L might be a promoter of LAD and could serve as a
predictor for LAD patients.
Keywords: CKAP2L,
prognosis, lung adenocarcinoma, migration, proliferation