108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

呋喃香豆素胺衍生物通过激活 Akt/GSK-3β/β-连环蛋白信号通路诱导黑素的生成
Authors Zang D, Niu C, Aisa HA
Received 20 July 2018
Accepted for publication 28 November 2018
Published 12 February 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 623—632
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S180960
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
Background: Melanogenesis,
or the biosynthesis of melanin, plays a critical role in the pigmentation of
skin, hair, and eyes. Reduced melanogenesis may lead to depigmentation
conditions such as vitiligo. Psoralen, a furocoumarin derivative, is closely
associated with melanogenesis, and its derivative 8-methoxypsoralen is used in
psoralen and ultraviolet A therapy for pigmentation disorders. In a previous
study, we synthesized a new series of amine derivatives of furocoumarin, of
which 5-(morpholinomethyl)-3-phenyl-7H -furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one (encoded as D206008) showed
a remarkable melanogenic effect in B16 murine cells.
Methods: In this
study, we examined the effects of D206008 on the melanogenesis-related pathways
in B16 cells. D206008 increased melanin production and tyrosinase (TYR)
activity, as well as the mRNA and protein expression levels of the melanogenic
enzymes TYR, TRP-1 and TRP-2, and the melanogenesis-related transcription
factor microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) in a
dose-dependent (0–100 µM) and time-dependent (0–48 hours) manner.
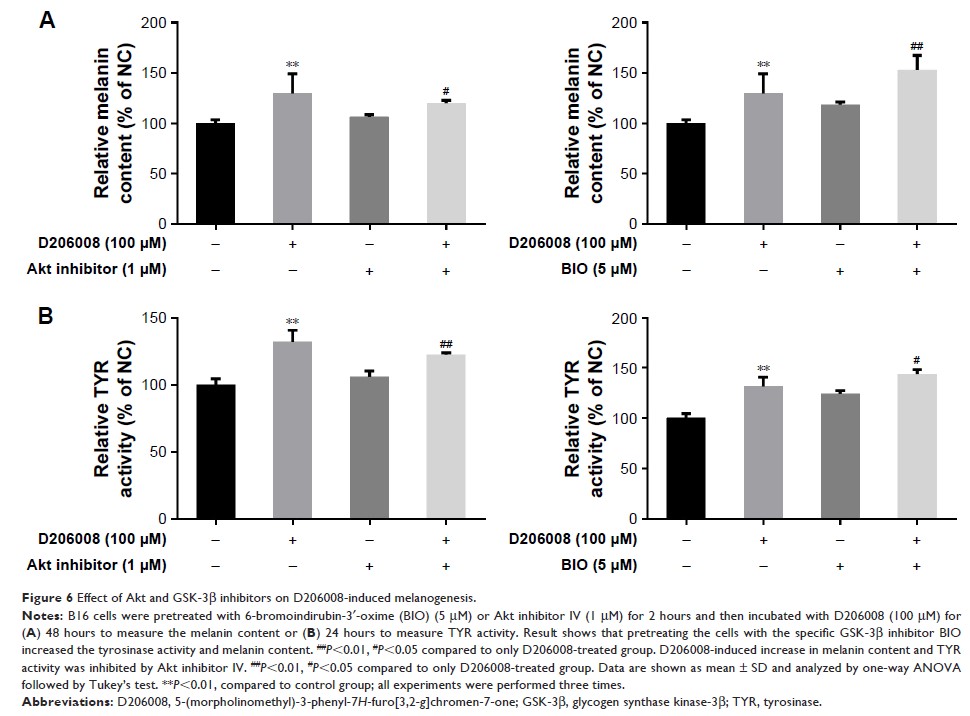
Results: Mechanistically,
D206008 inhibited β-catenin degradation by enhancing the phosphorylation of Akt
and glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β), which increased the accumulation of
β-catenin in the cytoplasm. Nuclear translocation of β-catenin also increased
in response to D206008 treatment.
Conclusion: Taken
together, these data indicate that D206008 promotes melanin synthesis by
stimulating the nuclear translocation of β-catenin, which activates MITF
transcription and eventually melanogenesis.
Keywords: amine derivatives
of furocoumarin, melanogenesis, Akt/GSK-3β/β-catenin