108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

环状 RNA circHIPK3 通过 miR-193a-3p 海绵作用和上调节 MCL1 表达来促进前列腺癌的细胞增殖和侵袭
Authors Chen D, Lu X, Yang F, Xing N
Received 12 October 2018
Accepted for publication 22 December 2018
Published 12 February 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1415—1423
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S190669
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ahmet Emre Eskazan
Background: While
emerging evidence indicates that circHIPK3 is critically involved in
tumorigenesis and the development of several cancers, its role in prostate
cancer (PCa) is not clearly understood.
Materials and methods: Human PCa
samples and their matched normal adjacent tissues were obtained from 26
patients to assess the expression of circHIPK3 and its relationship with PCa
prognosis. A series of in vitro and in vivo functional experiments were carried
out to elucidate the role of circHIPK3 in PCa progression and its underlying
molecular mechanisms.
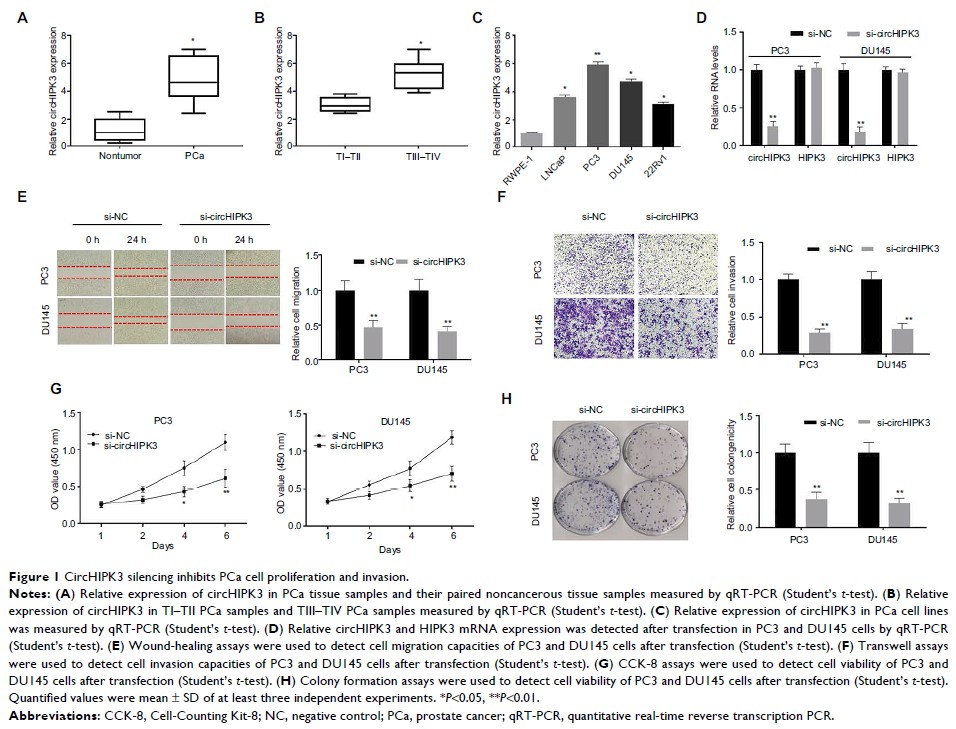
Results: In this
study, we found that circHIPK3 was overexpressed in PCa tissues and that higher
circHIPK3 expression was associated with tumor stage. Moreover, circHIPK3
knockdown markedly inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion of PCa
cells in vitro and impaired tumor growth in vivo. Bioinformatics analysis and
luciferase reporter assays demonstrated that circHIPK3 could promote MCL1
expression by interacting with miR-193a-3p in PCa. Finally, rescue assays
illustrated that circHIPK3 knockdown could partially reverse the effects of
MCL1 overexpression.
Conclusion: In
summary, our study illustrated, for the first time, that circHIPK3-mediated
miR-193a-3p-MCL1 signaling promotes PCa development and progression, providing
a novel therapeutic target for PCa.
Keywords: prostate
cancer, circular RNA, circHIPK3, miR-193a-3p, MCL1