108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

经激活的 Wnt signaling 在临床前研究模型中促进产甲胎蛋白胃癌的生长和进展
Authors Chen D, Lin X, Zhang C, An G, Li Z, Dong B, Shen L, Gao J, Zhang X
Received 11 September 2018
Accepted for publication 27 December 2018
Published 11 February 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1349—1362
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S187219
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Background: Characterized
by elevated AFP levels in serum, AFP-producing gastric cancer (APGC) is a very
special type of gastric cancer (GC) that is difficult to treat and has poor
prognosis. However, little is known about the role of AFP in GC, which was
investigated in this study with in vitro and in vivo experiments.
Methods: APGC
cells were established with lentivirus infection and validated by PCR assay and
ELISA in HCG27 and AGS cells. Cell growth, migration, and invasion were
determined by CCK8, transwell assays, and animal experiments. RNA sequencing,
Western blot, dual-luciferase-reporter assays, and RNA interference were
employed to understand mechanisms underlying AFP activity, followed by
therapeutic investigations for APGC.
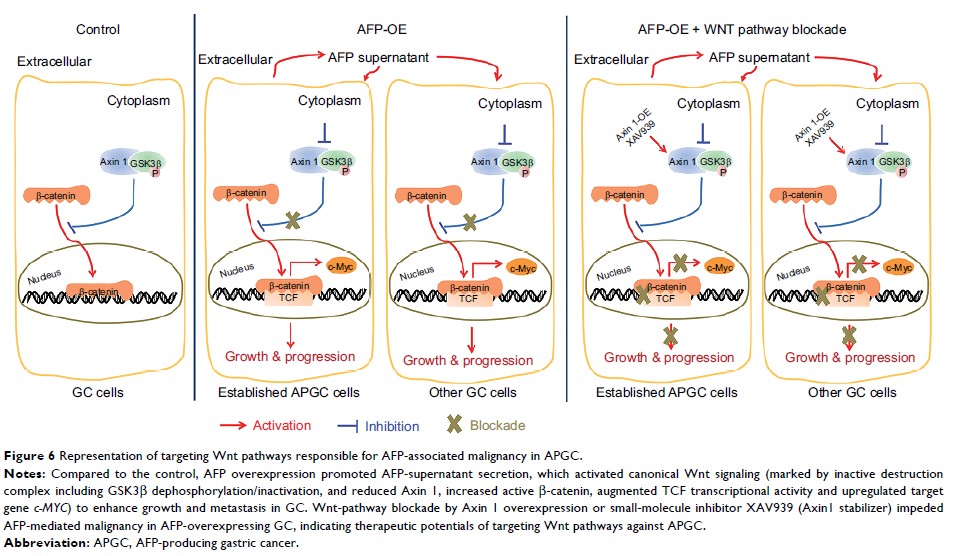
Results: APGC
cells featured significantly increased AFP levels in cellular supernatants. AFP
potentiated growth and aggression in GC cell lines and their derived
xenografts. Wnt-signaling activation was responsible for AFP function,
indicated by decreased Axin 1 and pGSK3β, followed by cascade activation of
β-catenin, downstream transcription factors TCF1/TCF7, and the target gene
– c-Myc .
Wnt-signaling blockade by Axin 1 rescue or pathway inhibitor XAV939 reversed
AFP function, suggesting the potential therapeutic value of APGC.
Conclusion: AFP played a
critical role in APGC through activating Wnt signaling, and targeting Wnt
pathways might be a promising strategy against APGC.
Keywords: alpha-fetoprotein,
AFP, AFP-producing gastric cancer, APGC, Axin 1, Wnt signaling, Wnt-signaling
inhibitor