109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
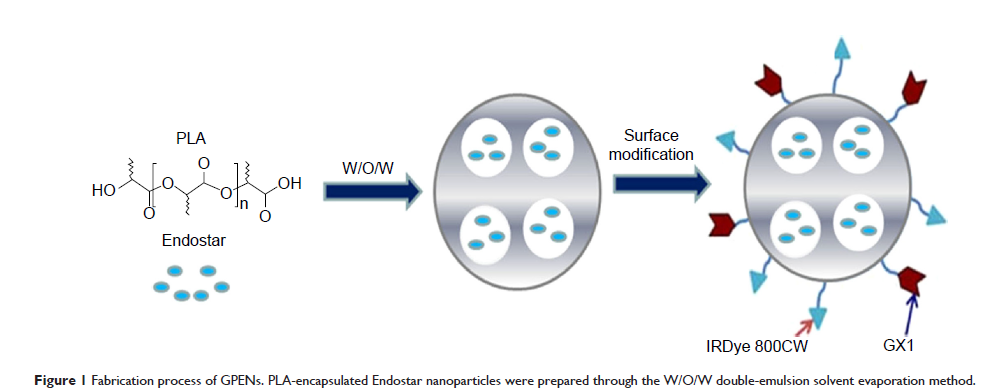
包埋恩度 (Endostar) 的 GX1 共轭聚 (乳酸) 纳米粒用于改善体内抗大肠癌治疗
Authors Du Y, Zhang Q, Jing L, Liang X, Chi C, Li Y, Yang X, Dai Z, Tian J
Published Date May 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 3791—3802
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S82029
Received 1 February 2015, Accepted 30 March 2015, Published 28 May 2015
Abstract: Tumor angiogenesis plays a key role in tumor growth and metastasis;
thus, targeting tumor-associated angiogenesis is an important goal in cancer
therapy. However, the efficient delivery of drugs to tumors remains a key issue
in antiangiogenesis therapy. GX1, a peptide identified by phage-display
technology, is a novel tumor vasculature endothelium-specific ligand and
possesses great potential as a targeted vector and antiangiogenic agent in the
diagnosis and treatment of human cancers. Endostar, a novel recombinant human
endostatin, has been shown to inhibit tumor angiogenesis. In this study, we
developed a theranostic agent composed of GX1-conjugated poly(lactic acid)
nanoparticles encapsulating Endostar (GPENs) and labeled with the near-infrared
dye IRDye 800CW to improve colorectal tumor targeting and treatment efficacy in
vivo. The in vivo fluorescence molecular imaging data showed that GPENs (IRDye
800CW) more specifically targeted tumors than free IRDye 800CW in colorectal
tumor-bearing mice. Moreover, the antitumor efficacy was evaluated by
bioluminescence imaging and immunohistology, revealing that GPENs possessed
improved antitumor efficacy on subcutaneous colorectal xenografts compared to
other treatment groups. Thus, our study showed that GPENs, a novel GX1 peptide
guided form of nanoscale Endostar, can be used as a theranostic agent to
facilitate more efficient targeted therapy and enable real-time monitoring of
therapeutic efficacy in vivo.
Keywords: GX1 peptide, Endostar, colorectal cancer, angiogenesis, IRDye 800CW, molecular imaging
Keywords: GX1 peptide, Endostar, colorectal cancer, angiogenesis, IRDye 800CW, molecular imaging