108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国患者安全事故报告制度的启示
Authors Gao XQ, Yan SP, Wu WQ, Zhang R, Lu YL, Xiao SY
Received 15 October 2018
Accepted for publication 10 January 2019
Published 8 February 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 259—267
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S190117
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Objective: We aimed
to explain the operational mechanism of China National Patient Safety Incidents
Reporting System, analyze patterns and trends of incidents reporting, and
discuss the implication of the incidents reporting to improve hospital patient
safety.
Design: A
nationwide, registry-based, observational study design.
Data source: The
database of China National Patient Safety Incidents Reporting System.
Outcome measures: Outcome
measures of this study included the temporal, regional, and hospital
distribution of the reports, as well as the incident type, location, parties,
and possible reasons for frequently occurring incidents.
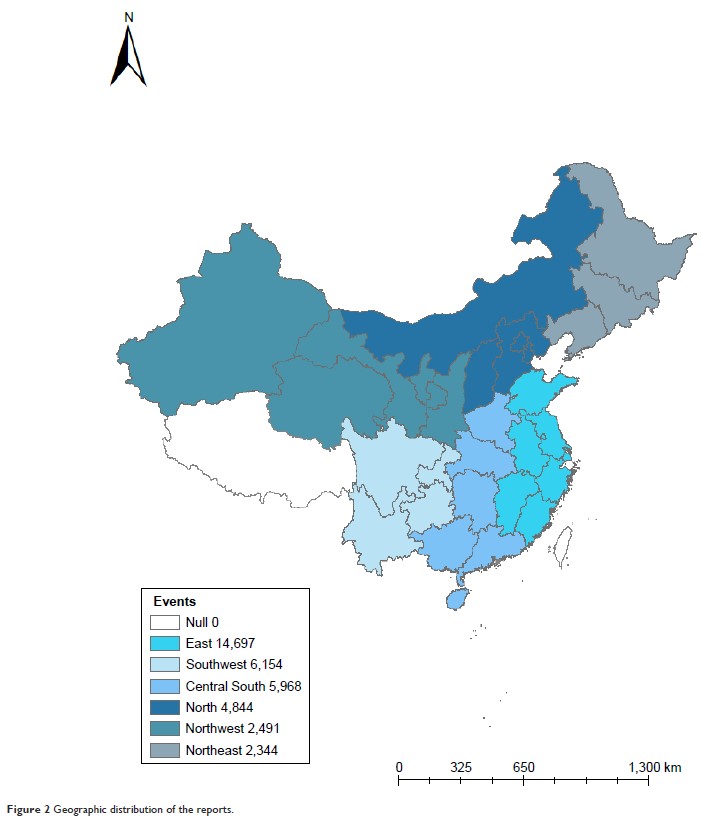
Results: During
2012–2017, 36,498 patient safety incidents were reported. By analyzing the time
trends, we found that there was a significant upward trend on incidents
reporting in China. The most common type of incidents was drug-related
incidents, followed by nursing-related incidents and surgery-related incidents.
The three most frequent locations of incident occurrence were Patient’s Room
(65.4%), Ambulatory Care Unit (8.4%), and Intensive Care Unit (7.4%). The
majority of the incidents involved nurses (40.7%), followed by physicians
(29.5%) and medical technologist (13.6%). About 44.4% of the incidents were
attributed to the junior staff (work experience ≤5 years). In addition,
incidents triggered by the senior staff (work experience >5 years) were more
often associated with severe patient harm.
Conclusion: To
strengthen the incidents reporting system and generate useful evidence through
learning from incidents reporting will be important to China’s success in
improving the nation’s patient safety status.
Keywords: patient
safety, NPSIRS, National Patient Safety Incidents Reporting System