108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Shugoshin1 的过度表达预示前列腺癌预后不良,并通过影响上皮 - 间质转化促进转移
Authors Mu J, Fan L, Liu D, Zhu D
Received 17 October 2018
Accepted for publication 17 January 2019
Published 8 February 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1111—1118
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S191157
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Objective: The aim
of the study was to investigate the role of shugoshinl (SGO1) in human prostate
cancer (PCa).
Materials and methods: Quantitative
real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to determine the expression of SGO1 in PCa
tissues and cell lines. The correlation between SGO1 expression and
clinicopathological characteristics of PCa patients was analyzed using
Kaplan–Meier analysis. SGO1 siRNA was successfully constructed and transfected
into PCa cell lines (LNCaP and PC3). The knockdown efficacy was assessed by
qRT-PCR. MTT assay and Transwell assay were conducted to observe the effect of
SGO1 on the proliferation and invasion of PCa cell lines.
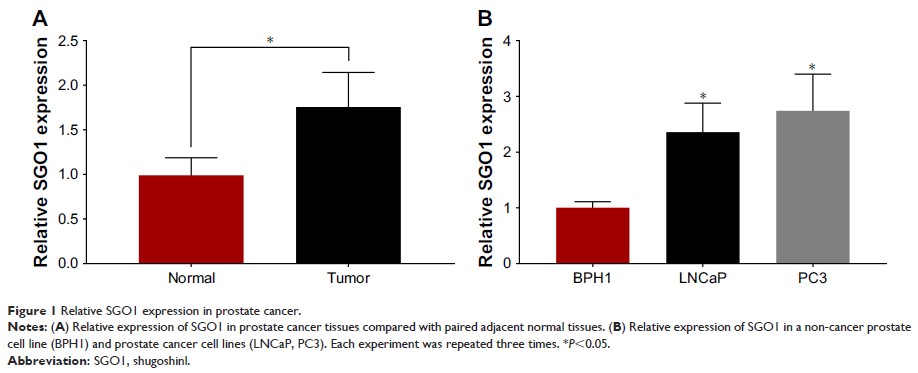
Results: SGO1-expression
levels were found to be higher in the PCa tissues and cell lines. Correlation
was identified between the expression of SGO1 and preoperative
prostate-specific antigen (P =0.017), lymph-node metastasis (P =0.044), and
Gleason score (P =0.041).
Patients with higher SGO1 expression displayed more advanced
clinicopathological characteristics in addition to a shorter biochemical
recurrence-free survival time. Additionally, SGO1 knockdown resulted in the
inhibition of PCa cell proliferation, migration, and invasion.
Conclusion: Taken
together, the findings of the current study present evidence suggesting that
SGO1 could inhibit the growth and invasion of PCa cells, highlighting its
potential as a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of PCa.
Keywords: shugoshinl,
prostate cancer, RNAi