108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

组织蛋白酶 G 使 IL-36γ 裂解和激活,同时引发牛皮癣的炎症
Authors Guo J, Tu J, Hu YY, Song GX, Yin ZQ
Received 15 November 2018
Accepted for publication 16 January 2019
Published 8 February 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 581—588
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S194765
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
Background: IL-36γ is
considered to be a valuable biomarker in psoriatic patients, which is expressed
as an inactive precursor that needs to be proteolytically processed and
activated, and neutrophil-derived proteases seemed to be potent activating
enzymes of IL-36γ.
Objectives: This
study aims to investigate the activation of IL-36γ by cathepsin G (CG) and
neutrophil elastase (NE).
Materials and methods: We used
inactive recombinant full-length (FL)-IL-36γ with different doses of NE or CG
to stimulate HaCaT cells; neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) were prepared
to act on FL-IL-36γ and then stimulate HaCaT cells. Real-time quantitative PCR
and ELISA were performed to detect CXCL-1 and CXCL-8 expression. We developed
imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like mouse model to evaluate the effect of
hypodermic injection of neutrophil-derived protease or its inhibitor.
Histopathology and Western blotting were conducted for effect assessment.
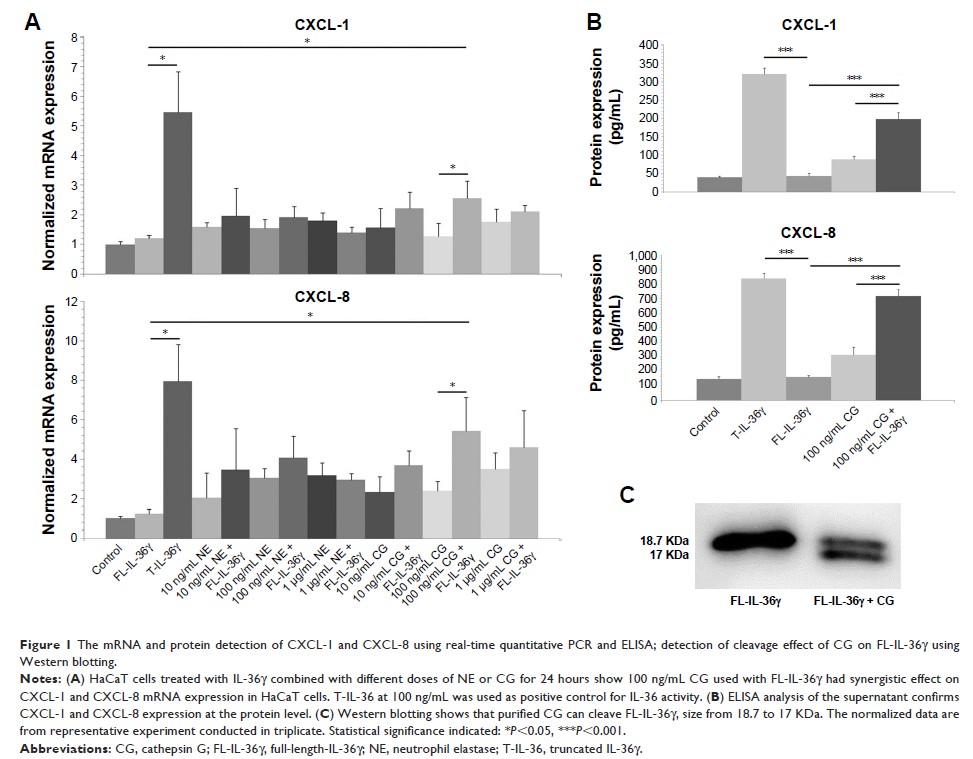
Results: Purified
CG cleaved and activated recombinant human FL-IL-36γ to promote CXCL-1 and CXCL-8
expression by human keratinocytes, and NETs activated FL-IL-36γ and the
activation was inhibited by serpin A3. CG induced expression of a more
truncated IL-36γ in psoriasiform lesion of mice and aggravated the
psoriasis-like lesion induced by imiquimod, whereas recombinant serpin A3
alleviated the severity of the psoriasis-like mouse mode.
Conclusion: CG has
the ability to cleave and activate IL-36γ and aggravate imiquimod-induced mouse
psoriasiform lesion. Thus, CG-specific inhibitors might be promising
therapeutic drugs for psoriasis.
Keywords: psoriasis,
IL-36, neutrophil, cathepsin, elastase