108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

DNA 甲基化介导的 miR-204 静默是甲状腺乳头状癌的潜在预后标志物
Authors Xia F, Wang W, Jiang B, Chen Y, Li X
Received 20 August 2018
Accepted for publication 8 January 2019
Published 8 February 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1249—1262
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S184566
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
Background: Papillary
thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is the most common endocrine malignancy and its
incidence has increased over the last few decades. The molecular mechanisms
underlying PTC tumorigenesis and progression are still unclear.
Patients and methods: The
microRNA (miRNA) expression patterns of PTC were revealed by miRNA microarray
analysis and validated with The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data. Promoter DNA
methylation rates of miR-204 were analyzed by Agena Methylation MassARRAY
analysis and validated with TCGA data. The underlying molecular mechanisms of
miR-204 involved in PTC were studied by bioinformatics analyses.
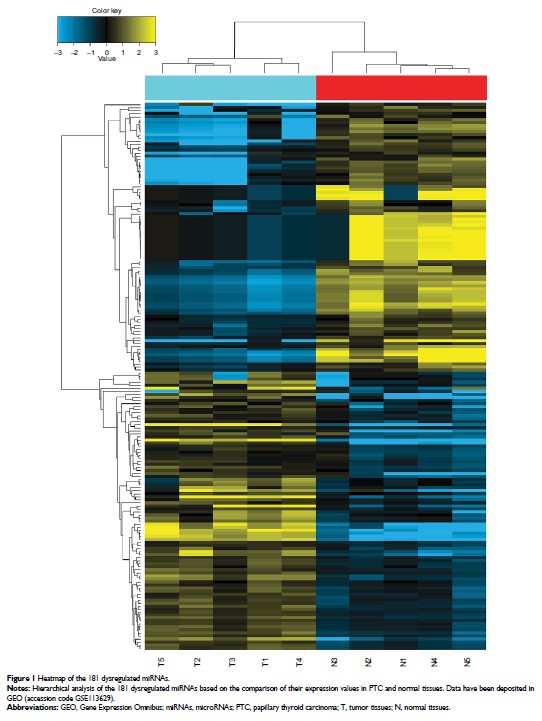
Results: A total
of 181 differentially expressed miRNAs (89 downregulated and 92 upregulated
miRNAs) between PTC and normal tissues were detected in this study. We
identified miR-204 as one of the most significantly downregulated miRNAs in
PTC. Downregulation of miR-204 was related to PTC extrathyroidal extension,
high T-stage, lymph metastasis, BRAF V600E mutation, and aggressive tall cell
variant. The Agena MassARRAY results indicated that 12 CpG sites located at the
promoter of miR-204 were hypermethylated in PTC tissues compared to normal
tissues. The promoter methylation rates of miR-204 in PTC were negatively
correlated with the expression levels of miR-204 and its host gene TRPM3 .
Downregulated miR-204 expression was related to several important pathways and
mechanisms involved in tumorigenesis and progression.
Conclusion: Promoter
DNA methylation-silenced miR-204 could serve as a potential diagnostic
biomarker of PTC. Downregulation of miR-204 may play an important role in PTC
via its involvement in many tumor-related pathways. Novel target genes and
putative mechanisms of miR-204 in PTC need to be further validated.
Keywords: papillary
thyroid carcinoma, miRNA, promoter DNA methylation, bioinformatics