108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

PTPN9 通过减轻 Stat3 的活化诱导细胞凋亡,并在结直肠癌中起肿瘤抑制剂的作用
Authors Wang D, Cheng Z, Zhao M, Jiao C, Meng Q, Pan H, Xie Y, Li L, Zhu Y, Wang W, Qu C, Liang D
Received 10 September 2018
Accepted for publication 8 January 2019
Published 8 February 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1309—1319
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S187001
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Background: Accumulating
evidence has shown that protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) are involved in
regulating the transduction of many signaling pathways and play important roles
in modulating the progression of some cancers, but the functions of PTPs in
cancers have not been well elucidated until now. Here, we aimed to identify the
roles of protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor type 9 (PTPN9), a cytoplasmic
PTP, in the development of colorectal cancer and elucidate the regulatory
mechanism involved.
Materials and methods: Cell
viability assessment, colony formation assay, caspase-3 and caspase-9 activity
assay, real-time PCR, and Western blot analysis were applied.
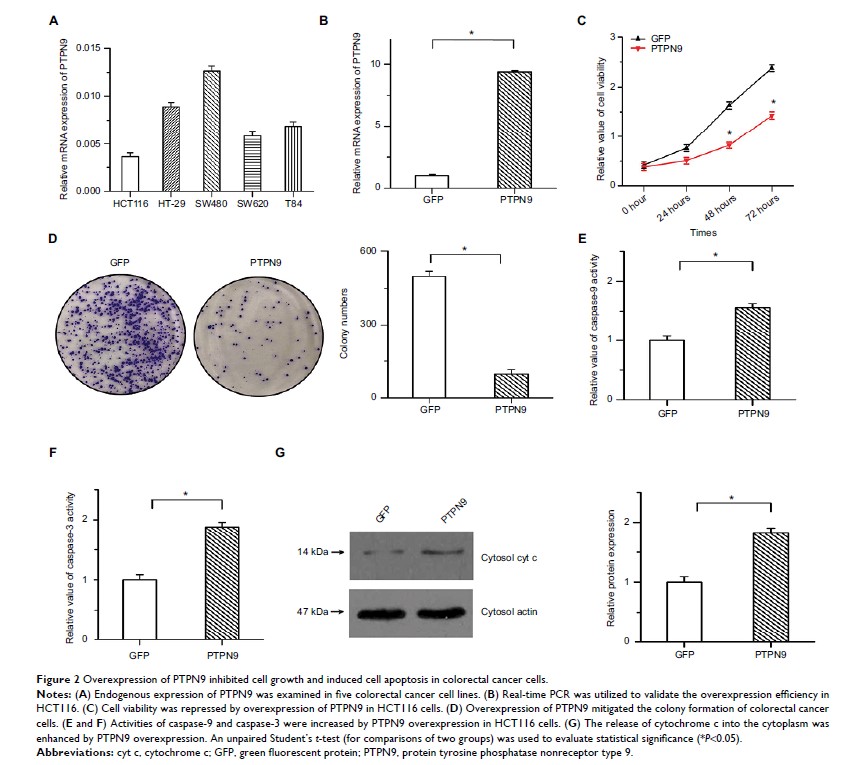
Results: Our
results showed that PTPN9 expression was frequently downregulated in colorectal
cancer tissues compared with adjacent normal tissues. Overexpression of PTPN9
mitigated cell growth and colony formation and induced cell apoptosis in
colorectal cancer. Conversely, PTPN9 knockdown promoted cell growth and
survival. Moreover, PTPN9 negatively regulated the activation of Stat3 and
depressed its nuclear translocation in colorectal cancer. The effects of PTPN9
knockdown on cell apoptosis were attenuated by inhibition of the Stat3 pathway.
Conclusion: These results
indicate that PTPN9 inhibits cell growth and survival by repressing the
activation of Stat3 in colorectal cancer, which suggests an important
underlying mechanism of regulating cell growth and provides a novel candidate
therapeutic target for colorectal cancer.
Keywords: PTPN9,
apoptosis, colorectal cancer, Stat3, cell survival, PTPMeg2