108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MWCNT 与蛋白质的相互作用:表面诱导的蛋白质吸附变化和蛋白质电晕对细胞摄取和细胞毒性的影响
Authors Zhang T, Tang M, Yao Y, Ma Y, Pu Y
Received 22 October 2018
Accepted for publication 15 January 2019
Published 7 February 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 993—1009
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S191689
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Purpose: Protein adsorption onto nanoparticles in
the form of protein corona, affects properties of nanomaterials and their
behavior in the biological milieu. This study aims at exploring the effects of
multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) surface chemistry on bovine serum albumin
(BSA) and immunoglobulin G (IgG), including their adsorption behavior and
spatial configurations, as well as the impact on cellular uptake, cytotoxicity,
and cellular responses.
Methods: Three
types of MWCNTs (pristine MWCNTs, MWCNTs-COOH, and MWCNTs-PEG) were synthesized
by classical chemical reduction. The size, morphology, hydrodynamic size, and
zeta potential were characterized using transmission electron microscopy and
dynamic light scattering. MWCNTs were exposed to BSA and IgG solutions, then
the amount of MWCNT absorption was performed by bicinchoninic acid assay, and
the effects were assessed by utilizing fluorescence spectroscopy, circular
dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. Quantitative measurement of MWCNTs uptake with or
without protein corona was performed as turbidity method. CCK assay and a
microdilution method were performed to evaluate the effects of protein corona
on cytotoxicity and pro-inflammatory cytokines release.
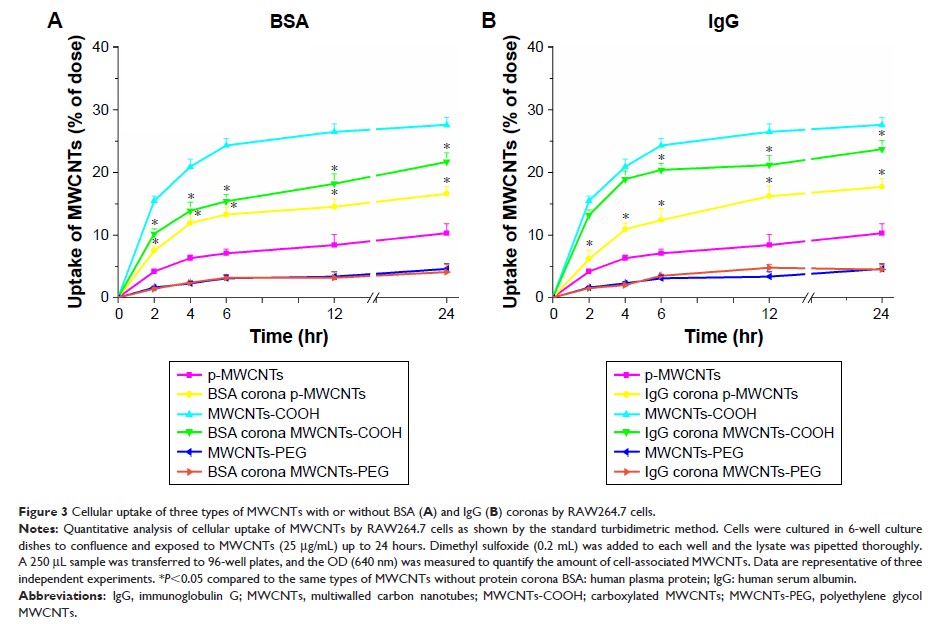
Results: The
BSA and IgG adsorption capacities of MWCNTs followed the order pristine
MWCNTs>MWCNTs-COOH and MWCNTs-PEG. MWCNT binding can cause fluorescence
quenching and conformational changes in BSA and IgG, indicating that both the
physicochemical properties of MWCNTs and protein properties play critical roles
in determining their adsorption behavior. Further study showed time-dependent
increases in MWCNT cellular uptake and internalization. Hydrophobicity is the
major factor increasing cellular uptake of pristine MWCNTs, but a protein
corona enriched with dysoposnins is the main factor reducing uptake of MWCNT-COOH
by RAW264.7 cells. The cytotoxicity and pro-inflammatory response related to
physicochemical properties of MWCNTs, and frustrated phagocytosis is a key
initiating event in the pro-inflammatory response of MWCNT-exposed
macrophages.
Conclusion: These
findings shed light on how functionalized MWCNTs interact with protein coronas
and provide useful insight into the dramatic effect of protein coronas on
different functionalized MWCNTs. These events affect cellular uptake and
cytotoxicity, which could inform how to enhance MWCNT biocompatibility and
develop approaches for managing MWCNT hazards.
Keywords: multiwalled
carbon nanotubes, protein corona, cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, inflammation