108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

超声引导细针穿刺甲状腺结节(最大直径小于 10 mm)活检:尺寸重要吗?
Authors Lyu Y, Shen F, Yan Y, Situ M, Wu W, Jiang G, Chen Y
Received 1 October 2018
Accepted for publication 8 January 2019
Published 7 February 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1231—1236
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S189358
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
Objective: Ultrasound-guided
fine-needle aspiration biopsy (US-FNAB) is a safe and effective method of
screening malignant thyroid nodules such as papillary thyroid carcinoma.
However, not much data are available regarding the diagnostic efficacy of
US-FNAB for papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (≤10 mm in diameter). We aim to
compare the diagnostic efficacy of US-FNAB on thyroid nodules between two
groups divided by a diameter of 10 mm by correlating the cytological results of
US-FNAB with the histopathologic diagnoses in selected patients.
Patients and methods: Eight
hundred twenty-two thyroid nodules (Group A: diameter ≤10 mm, n=620; Group B:
diameter >10 mm, n=202) from 797 patients treated between March 2014
and June 2017 were retrospectively evaluated. Only nodules with Thyroid Imaging
Reporting and Data System (TIRADS) categories 4–6 were enrolled and sampled by
US-FNAB, followed by surgical resection.
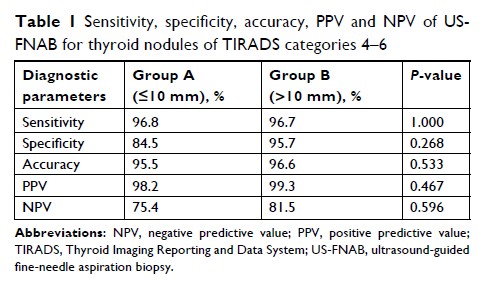
Results: According
to The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology (TBSRTC) diagnostic
categories, 94 thyroid nodules were classified as I, III and IV, and were
excluded from the analysis. The resultant 728 thyroid nodules from 721 patients
were analyzed. The malignant tendency (TBSRTC V and VI) rates on US-FNAB were
88.2% and 84.6% (P =0.202) in Group A and Group B, respectively, and the
malignant rates were 89.5% and 86.9% (P =0.330), respectively, on histopathology. There was a
high concordance between cytology and histopathology diagnoses (kappa value
=0.797), and no statistical difference in terms of US-FNAB accuracy was found
between the two groups (P =0.533).
Conclusion: For
thyroid nodules of TIRADS category 4–6, the diagnostic efficacy of US-FNAB is
similar for thyroid nodules either smaller or greater than 10 mm in their
maximum diameter.
Keywords: ultrasound-guided
fine-needle aspiration biopsy, thyroid nodules, microcarcinoma, histopathology,
cytopathology