108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Nrf2/HO-1 轴可以成为透明细胞肾细胞癌的预后因子
Authors Deng Y, Wu Y, Zhao P, Weng W, Ye M, Sun H, Xu M, Wang C
Received 19 September 2018
Accepted for publication 3 January 2019
Published 7 February 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1221—1230
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S188046
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Objective: To study
the protein expression level of Nrf2/HO-1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
(ccRCC) and adjacent normal tissue and to explore its relationship with
clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis in ccRCC patients.
Materials and methods: In total,
152 ccRCC patients with available follow-up and clinical data were enrolled,
and sample microarrays were prepared for immunohistochemistry studies. The
human ccRCC cell lines 786-O, OS-RC-2, A498, and ACHN were cultured for
immunofluorescence. The protein concentrations of five ccRCC patients’ tumor
and adjacent normal renal tissues were prepared for Western blotting.
Chi-squared tests, Fisher’s exact test, Kaplan–Meier analyses, log-rank tests,
and Cox regression were performed for statistical analyses.
Results: The
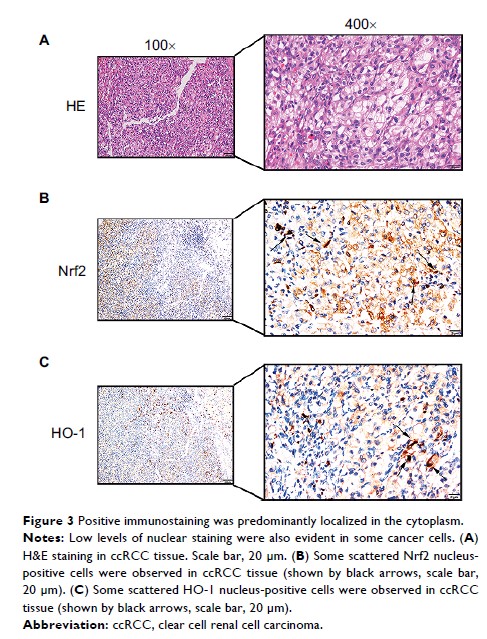
immunoreactivity results showed that the Nrf2 and HO-1 proteins were found in
consistent locations in vitro and were expressed both in ccRCC and adjacent
normal tissues. The two proteins were localized in the cytoplasm and nucleus of
RCC tumor cells and in adjacent normal tissue cells. The expression levels of
Nrf2 and HO-1 were significantly higher in ccRCC tissues than in the adjacent
normal tissues. The Nrf2 protein level was found to be significantly correlated
with the tumor size. Additionally, higher protein expression levels of Nrf2 and
HO-1 were also correlated with worse overall survival outcomes and could
potentially be used to predict the prognosis of ccRCC patients.
Conclusion: Our study
provides an important theoretical basis for evaluating the clinical prognosis
of ccRCC patients, which implies that the Nrf2/HO-1 axis can be a prognostic
factor in ccRCC.
Keywords: ROS,
Nrf2, HO-1, immunohistochemistry, prognosis