108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

双胶束负载明胶纳米纤维及其在脂多糖诱导的牙周病中的应用
Authors Wang Y, Li H, Feng Y, Jiang P, Su J, Huang C
Received 31 July 2018
Accepted for publication 22 November 2018
Published 5 February 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 963—976
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S182073
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
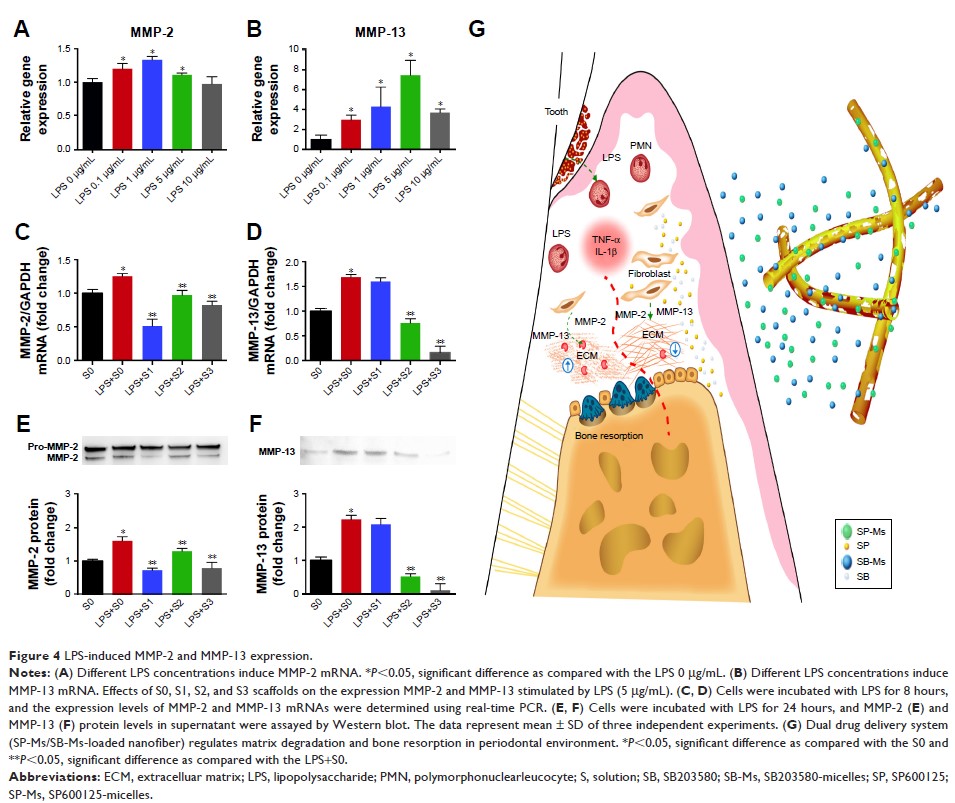
Introduction: Combined
therapies utilizing inhibitors to remove pathogens are needed to suppress
lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced periodontal disease. We prepared a novel, multi-agent
delivery scaffold for periodontal treatment.
Methods: In this
study, we synthesized SP600125 (a JNK inhibitor) and SB203580 (a p38 inhibitor)
drug-loaded poly(ethylene glycol)-block-caprolactone copolymer via dialysis
method. The physical property of micelles was characterized through dynamic
light scattering and transmission electron microscopy. The cell growth and
LPS-induced MMP-2 and MMP-13 expression were evaluated through CCK-8, real-time
PCR and Western blot assay. The release of SP600125 and SB203580 from different
scaffolds was estimated. Microcomputed tomography and histology were used for
evaluating the effect of the micelles-loaded nanofibers on the treatment of
class II furcation defects in dogs.
Results: The drug
was then successfully incorporated into gelatin fibers during electrospinning
process. We confirmed that the micelles had spherical structure and an average
particle size of 160 nm for SP600125-micelles (SP-Ms) and 150 nm for
SB203580-micelles (SB-Ms). The nanofiber scaffold showed excellent
encapsulation capability, in vitro drug-release behavior, and cell
compatibility. Real-time PCR and Western blot assay further indicated that
LPS-induced MMP-2 and MMP-13 expression was significantly inhibited by the
scaffold.
Conclusion: The
results suggested that the dual drug-loaded system developed in this study
might become a highly effective therapy for periodontal disease.
Keywords: periodontal
disease, controlled release, drug-loaded micelles, electrospun nanofibers,
scaffold