108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Longdaysin 抑制 Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号传导并显示出抗乳腺癌的抗肿瘤活性
Authors Xiong Y, Zhou L, Su Z, Song J, Sun Q, Liu SS, Xia Y, Wang Z, Lu D
Received 1 November 2018
Accepted for publication 8 December 2018
Published 5 February 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 993—1005
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S193024
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Background: CK1 is
involved in regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling and represents a promising
target for the treatment of breast cancer. A purine derivative longdaysin has
recently been identified as a novel modulator of cellular circadian rhythms
through targeting the protein kinases CK1δ, CK1α, and ERK2. However, the
antitumor activity of longdaysin and its underlying mechanisms remain unclear.
Methods: The
inhibitory effect of longdaysin on Wnt/β-catenin signaling was investigated
using the SuperTOPFlash reporter system. The levels of phosphorylated LRP6,
total LRP6, DVL2, active β-catenin, and total β-catenin were examined by
Western blot. The expression of Wnt target genes was determined using real-time
PCR. The ability of colony formation of breast cancer cells was measured by
colony formation assay. The effects of longdaysin on cancer cell migration and
invasion were assessed using transwell assays. The effect of longdaysin on
cancer stem cells was tested by sphere formation assay. The in vivo antitumor
effect of longdaysin was evaluated using MDA-MB-231 breast cancer xenografts.
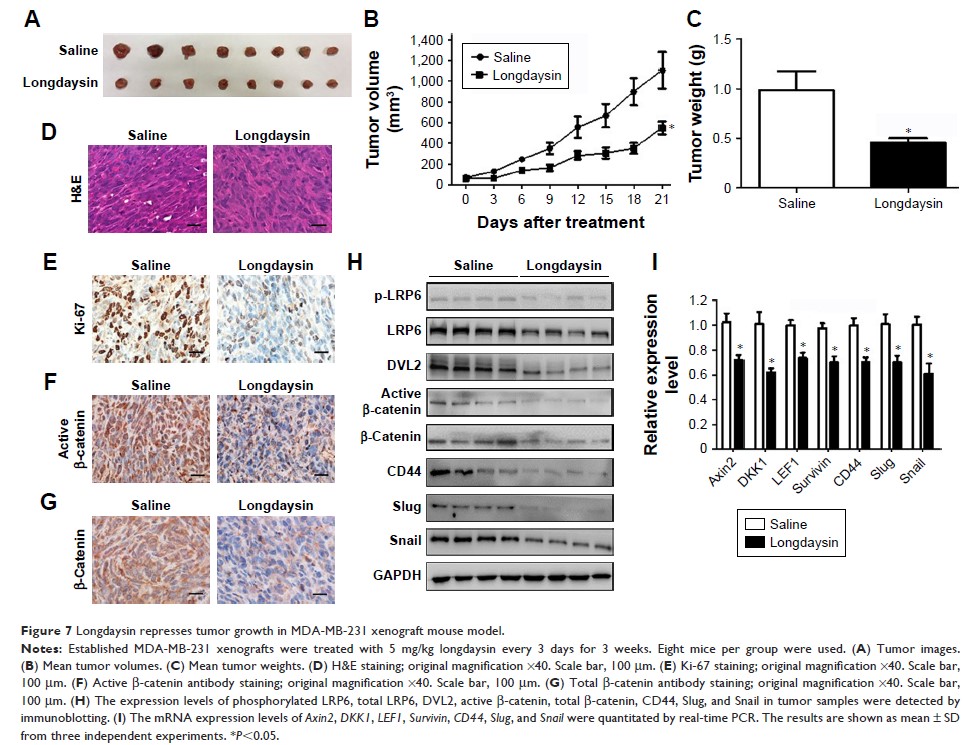
Results: Longdaysin
suppressed Wnt/β-catenin signaling through inhibition of CK1δ and CK1ε in
HEK293T cells. In breast cancer Hs578T and MDA-MB-231 cells, micromolar
concentrations of longdaysin attenuated the phosphorylation of LRP6 and DVL2
and reduced the expression of active β-catenin and total β-catenin, leading to
the downregulation of Wnt target genes Axin2 , DKK1 , LEF1 , and Survivin . Furthermore, longdaysin inhibited the
colony formation, migration, invasion, and sphere formation of breast cancer
cells. In MDA-MB-231 breast cancer xenografts, treatment with longdaysin
suppressed tumor growth in association with inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin
signaling.
Conclusion: Longdaysin
is a novel inhibitor of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. It exerts
antitumor effect through blocking CK1δ/ε-dependent Wnt signaling.
Keywords: longdaysin,
Wnt, β-catenin signaling, CK1δ, CK1ε, breast cancer