108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

减毒的 ZHX3 表达作为潜在的生物标志物预测乳腺癌患者的不良临床结果
Authors You Y, Ma Y, Wang Q, Ye Z, Deng Y, Bai F
Received 17 August 2018
Accepted for publication 4 January 2019
Published 5 February 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1199—1210
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S184340
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 1
Editor who approved publication: Dr Rituraj Purohit
Background: The ZHX
family has recently been in the spotlight as an integrator and an indispensable
node in carcinogenesis, whose expression is frequently dysregulated in multiple
cancers. The current study provides a novel investigation of the expression
profiles of ZHX factors in breast cancer.
Materials and methods: The mRNA
levels of ZHXs and follow-up periods in breast cancer patients were mined
through the Oncomine, Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia, bc-GenExMiner, cBioPortal
and Kaplan–Meier plotter databases. In addition, ZHX3 protein expression was
examined in 98 primary tumor samples by immunohistochemistry to investigate its
association with clinicopathological parameters and patient outcomes.
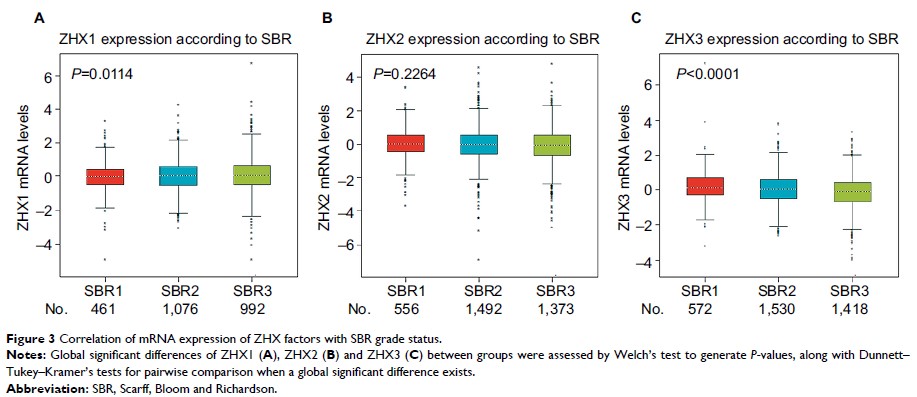
Results: We found
that the transcriptional levels of ZHX1, ZHX2 and ZHX3 were not significantly
altered in tumor tissues compared with those in nontumor tissues. ZHX2 and ZHX3
mRNA levels were observed to be positively correlated with estrogen receptor
and progesterone receptor expression, while ZHX2 mRNA levels were negatively
associated with HER2 expression. Survival analyses revealed that high mRNA
levels of ZHX2 and ZHX3 correlated with better overall survival in patients
with breast cancer. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed that patients with
decreased ZHX3 protein levels had poorer outcomes. Multivariate analysis
exhibited that ZHX3 expression may serve as an independent high-risk prognostic
predictor.
Conclusion: Dysregulated
expression of ZHXs may be involved in the progression of breast cancer and
could serve as a novel biomarker and potential target for breast cancer.
Keywords: ZHX,
breast cancer, data mining, immunohistochemistry, prognosis