108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Patlak 模型动态增强磁共振成像(Patlak 模型)检测复发缓解型多发性硬化症的脑通透性和灌注特征
Authors Xiong H, Yin P, Li X, Yang C, Zhang D, Huang X, Tang Z
Received 3 October 2018
Accepted for publication 27 December 2018
Published 4 February 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 233—240
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S189598
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
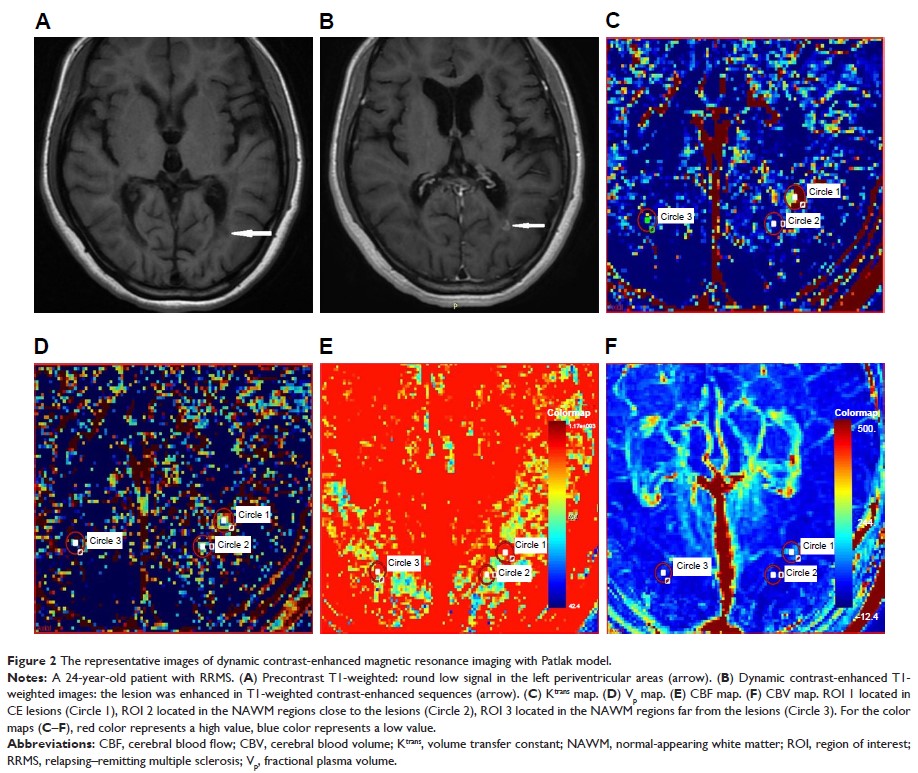
Objective: To
investigate the features of cerebral permeability and perfusion detected by
dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) with Patlak
model in relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) and their correlations
with Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) scores and disease duration.
Patients and methods: Twenty-seven
RRMS patients underwent conventional MRI and DCE-MRI with 3.0 T magnetic
resonance scanner were enrolled in the study. A Patlak model was used to
quantitatively measure MRI biomarkers, including volume transfer constant (Ktrans), fractional
plasma volume (Vp), cerebral blood flow (CBF), and cerebral
blood volume (CBV). The correlations of MRI biomarkers with EDSS scores and
disease duration were analyzed.
Results: The MRI
biomarkers Ktrans, Vp, CBF, and CBV
of contrast-enhancing (CE) lesions were significantly higher (P <0.05) than
those of non-enhancing (NE) lesions and normal-appearing white matter (NAWM)
regions. The skewness and kurtosis of Ktrans values in
CE lesions were significantly higher (P <0.05) than that of NE lesions. No significant
correlation was found among the biomarkers with EDSS scores and disease
duration (P >0.05).
Conclusion: Our study
demonstrated the abnormalities of permeability and perfusion characteristics in
multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions and NAWM regions by DCE-MRI with Patlak model.
The Ktrans, Vp, CBF, and CBV
of CE lesions were significantly higher than that of NE lesions, but these MRI
biomarkers did not associate with the severity and duration of the disease. The
skewness and kurtosis of Ktrans value in
CE lesions were significantly higher than that in NE lesions, indicating that
these parameters of Ktrans histogram
can be used to distinguish the pathology of MS lesions.
Keywords: dynamic
contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging, Patlak model, multiple sclerosis,
permeability, perfusion, histogram