108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

氯胺酮的神经保护潜力可防止异氟醚经由 PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β 通路导致脑结构损伤及诱导神经认知功能改变
Authors Wang R, Zhang Z, Kumar M, Xu G, Zhang M
Received 25 September 2018
Accepted for publication 20 November 2018
Published 4 February 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 501—512
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S188636
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Background: The aim
of the current experimental study was to scrutinize the neuroprotective effect
of ketamine on the isoflurane (iso)-induced cognitive dysfunction in rats via
phosphoinositide 3 kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT)/glycogen synthase
kinase 3β (GSK-3β) pathway.
Materials and methods: Sprague-Dawley
rats were used for the current experimental study. The rats were divided into
six groups and rats were treated with ketamine and memantine. For the
estimation of cognitive function study, we used the Morris water test.
Pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-α
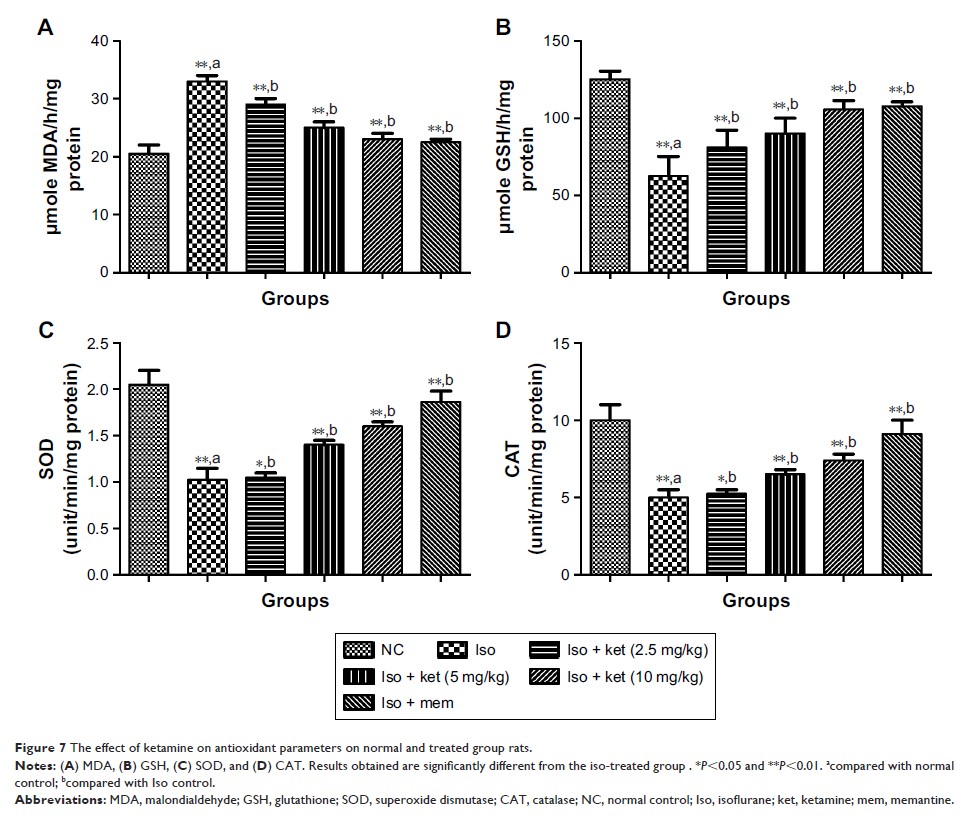
(TNF-α), and caspase-6; the antioxidant parameters malondialdehyde,
glutathione, superoxide dismutase, catalase, and protein carbonyl;
acetylcholinesterase, amyloid β, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor were
estimated, respectively. The protein expression of AKT, GSK-3β, p21WAF1/CIP1,
and p53 was also estimated, respectively.
Results: Ketamine
significantly enhanced cognitive function and showed anti-inflammatory and
antioxidant effects, and exhibited the neuroprotective effect of ketamine
against the isoflurane-induced cognitive impairment. Additionally, ketamine
significantly (P <0.005)
suppressed IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, caspase-6 and p21WAF1/CIP1, p53 expression and
up-regulated the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β expression in the group of iso-induced rats.
Conclusion: We can
conclude that ketamine prevented the cognitive impairment induced by isoflurane
anesthesia through anti-apoptotic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects
via the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway.
Keywords: ketamine,
isoflurane, neuroinflammatory, PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway, cognitive impairment