108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

RACK1 的下调表达导致胰腺癌生长和转移
Authors Zhang L, Lv Y, Rong Y, Chen W, Fang Y, Mao W, Lou W, Jin D, Xu X
Received 1 June 2018
Accepted for publication 5 December 2018
Published 1 February 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1007—1020
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S176101
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Background: The expression and function of the
Receptor for Activated C Kinase 1 (RACK1) in cancer growth and metastasis are
confused in different cancers, especially in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
(PDAC).
Methods: One-hundred
and eighty-two PDAC tissue specimens (95 males and 87 females) including
pancreatic cancer tissue and para-carcinoma tissue were collected for analysis
between 2005 to 2012. Blood phenotypic parameters using cell count and
capillary electrophoresis were investigated. HE staining, real time PCR,
Western blot analysis, and soft agar assays were performed to determine the
role of RACK1.
Purpose: In
this study, we aim to determine the specific role of RACK1 in the untility of
PDAC.
Results: We
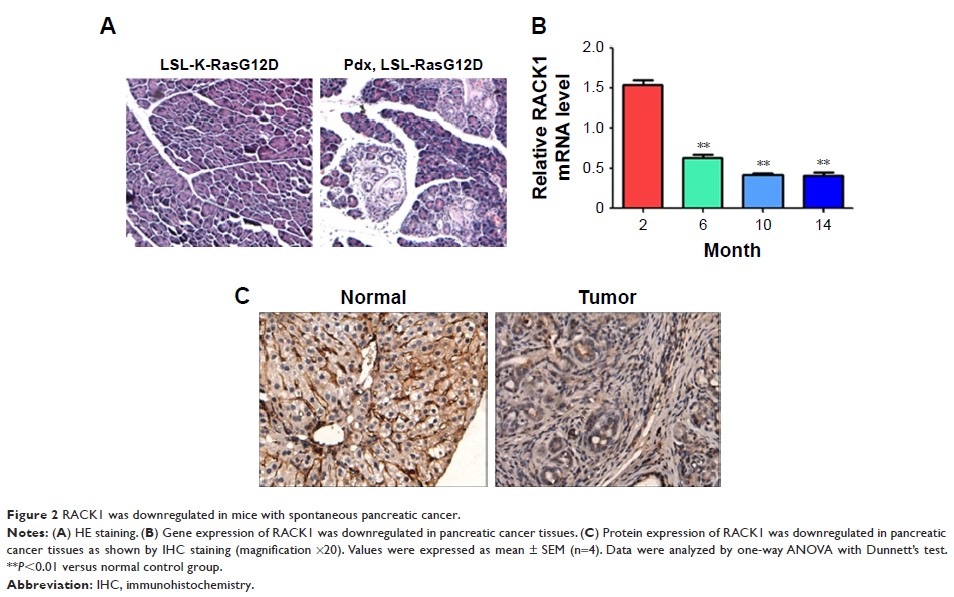
found that RACK1 expression was significantly lower in pancreatic cancer tissue
than in para-carcinoma normal pancreatic tissue both in clinic and mice with
pancreatic cancer at the early stage. Our results suggested that RACK1 silence
could significantly promote cell growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer
cells. But we found that the overexpression of RACK1 has the opposite effect in
vitro. In vivo MIAPaca-2 cells overexpressing RACK1, the results demonstrated
lower metastatic ability than MIAPaca-2 cells. RACK1 overexpression could
decrease the NF-κB transactivation activity of MIAPaca-2 cells, which was
consistent with the inhibitory effect of RACK1 overexpression on the pro-migration
and pro-invasive target gene of NF-κB, while which could be increased by RACK1
silence. RACK1 silence also enhanced protein expression of pro-migration and
pro-invasive NF-κB target genes, which on the contrary, could be reversed by
IκBα. Besides, RACK1 expression was significantly associated with lymph node
metastasis, vessels metastasis, invasion of nerves as well as TNM staging. The
3-year survival rate of patients with high RACK1 expression was significantly
higher than those patients with low RACK1 expression. However, RACK1 expression
was not an independent risk factor for of the long-term postoperative survival
of patients with pancreatic cancer.
Conclusion: The
obtained results in our study suggested that the low expression of RACK1 was
associated with cancer cell growth and metastasis in pancreatic cancer through
the activation of the NF-κB pathway. RACK1 could be a potential therapeutic
drug target to pancreatic cancer and metastasis.
Keywords: receptor
for activated C kinase 1, pancreatic cancer, NF-κB, in vivo