108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

ZNF433 正向调节前列腺癌中的 β-连环蛋白/TCF 通路并增强癌细胞的致瘤性
Authors Gu S, Hou P, Liu K, Niu X, Wei B, Mao F, Xu Z
Received 25 June 2018
Accepted for publication 26 November 2018
Published 1 February 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1031—1039
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S178150
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Background: Prostate
cancer often shows the over-activation of beta-catenin/t-cell factor (TCF)
signaling. It remains largely unknown how the beta-catenin/TCF transcriptional
machinery is tightly controlled.
Methods: The
ZNF433 mRNA and protein levels in the clinical tissues were examined using
q-PCR, Western blot and immunohistochemistry. The phenotypes of prostate cancer
cells were examined using MTT assay, Boyden chamber assay and
anchorage-independent assay. The interaction between ZNF433 and beta-catenin
was evaluated by immunoprecipitation.
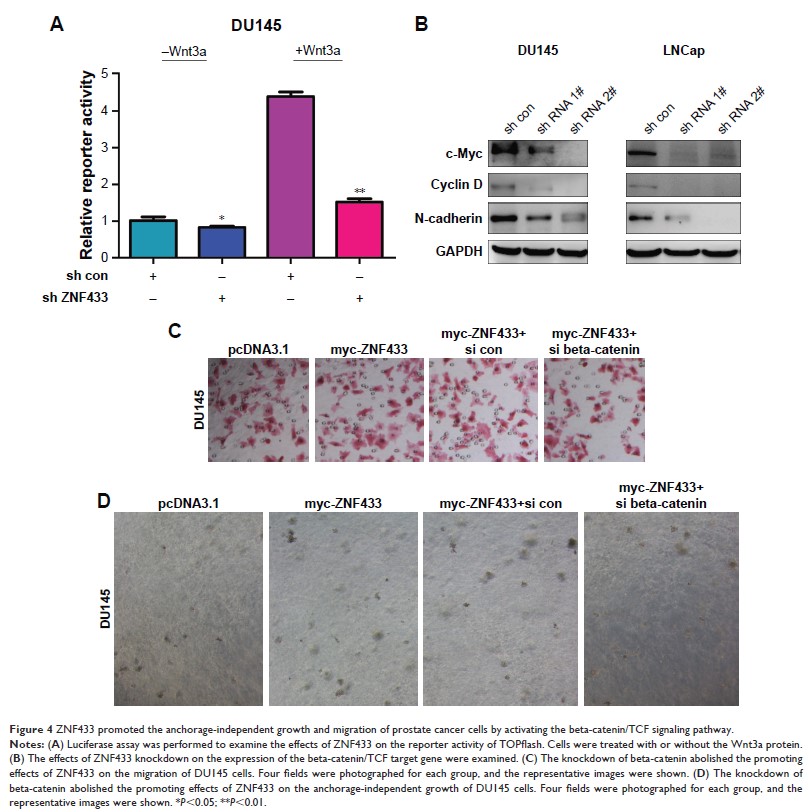
Results: In the
present study, ZNF433 was upregulated in prostate cancer samples, and promoted
the growth and migration of prostate cancer cells. Furthermore, ZNF433 was the
binding partner of beta-catenin and activated beta-catenin/TCF signaling in
prostate cancer. Moreover, ZNF433 enhanced the binding between beta-catenin and
TCF4. In addition, NC043, small antagonist for beta-catenin/TCF complex,
inhibited the malignant behaviors of prostate cancer cells driven by ZNF433.
Conclusion: In
summary, these studies demonstrate the tumor-promoting roles of ZNF433 in
prostate cancer, and suggesting that ZNF433 was a potential target for the
treatment.
Keywords: ZNF433,
beta-catenin, prostate cancer, motility