108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

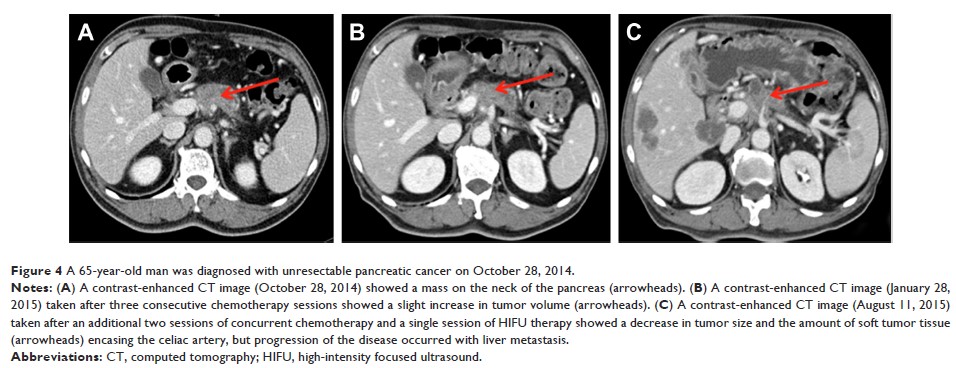
HIFU 在胰腺癌患者中是安全、有效和可行的:523 例患者的单中心回顾性研究
Authors Ning Z, Xie J, Chen Q, Zhang C, Xu L, Song L, Meng Z
Received 27 August 2018
Accepted for publication 27 November 2018
Published 1 February 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1021—1029
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S185424
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
Purpose: This
study aimed to evaluate the clinical value of high-intensity focused ultrasound
(HIFU) combined with gemcitabine (GEM) in treating unresectable pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
Patients and methods: A total
of 523 unresectable PDAC patients were recruited from December 30, 2007 to
January 30, 2015 at Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center. Among them, 347
received HIFU combined with GEM (with regional intra-arterial chemotherapy
[RIAC] or with systemic chemotherapy) and the remaining patients received GEM
only. Postoperative complications were observed, and overall survival was
recorded.
Results: The
median overall survival of patients who received HIFU combined with GEM vs GEM
alone was 7.4 vs 6.0 months (P =0.002); the 6-month, 10-month, 1-year, and 2-year
survival rates for patients in these two groups were 66.3% vs 47.5% (P <0.0001),
31.12% vs 15.9% (P <0.0001), 21.32% vs 13.64% (P =0.033), and 2.89%
vs 2.27% (P =0.78),
respectively. In the combined therapy group, the most obvious survival benefits
were obtained among patients who received HIFU plus RIAC and systemic
chemotherapy (used in the intervals between RIAC treatments). There were no
severe complications in patients undergoing HIFU treatment.
Conclusion: We
demonstrated the survival benefit of HIFU among PDAC patients treated with GEM.
The benefit was most obvious in PDAC patients treated with HIFU plus RIAC and
systemic chemotherapy.
Keywords: PDAC,
HIFU, multimodality therapy, gemcitabine, prognosis