108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

大黄酸通过抑制 STAT3 途径通路显示出抗非小细胞肺癌的有效功效
Authors Yang L, Li J, Xu L, Lin S, Xiang Y, Dai X, Liang G, Huang XY, Zhu J, Zhao C
Received 18 April 2018
Accepted for publication 17 December 2018
Published 1 February 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1167—1176
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S171517
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Nakshatri
Background: Non-small-cell
lung cancer (NSCLC) comprises about 85% of all lung cancers and is usually
diagnosed at an advanced stage with poor prognosis. The IL-6/STAT3 signaling
pathway plays a pivotal role in NSCLC biology. Rhein is a lipophilic
anthraquinone extensively found in medicinal herbs. Emerging evidence suggests
that Rhein has significant antitumor effects, supporting the potential uses of
Rhein as an antitumor agent.
Methods: Cell
viability and colony formation were performed to examine Rhein’s potent
antiproliferative effect in human NSCLC cell lines PC-9, H460 and A549. Flow
cytometry-based assay was employed to study whether Rhein could affect cell
apoptosis and cycle. The expression level of P-STAT3, apoptosis and
cycle-related proteins Bcl-2, Bax, MDM2, CDC2, P53 and CyclinB1 were detected
by Western blotting. The xenograft models were used to evaluate the in vivo
effect of Rhein.
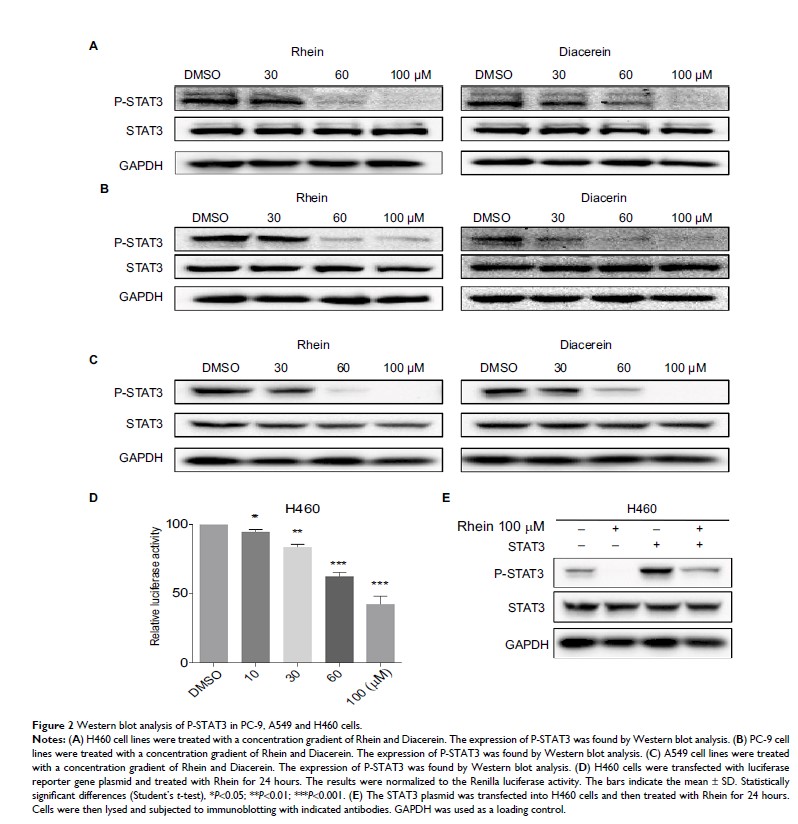
Results: We found
that Rhein could significantly reduce the viability and stimulate apoptosis in
human NSCLC cells in a dose-dependent manner. Western blot analysis results
suggested that the antitumor effect of Rhein might be mediated via STAT3
inhibition. Rhein upregulated the expression of the proapoptotic protein Bax
and downregulated the expression of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2. In
addition, Rhein induced the arrest of NSCLC cells in the G2/M phase of the cell
cycle and dose dependently inhibited the expression of cycle-related proteins.
The Rhein also inhibited tumor growth in H460 xenograft models.
Conclusion: Rhein
shows potent efficacy against NSCLC through inhibiting the STAT3 pathway. Our
results also suggest that Rhein has a promising potential to be used as a novel
antitumor agent for the treatment of NSCLC.
Keywords: Rhein,
NSCLC, STAT3, EGFR, diacerein, apoptosis, inhibitor