108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-600 通过下调 METTL3 的表达来抑制肺癌
Authors Wei W, Huo B, Shi X
Received 21 July 2018
Accepted for publication 21 December 2018
Published 1 February 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1177—1187
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S181058
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 1
Editor who approved publication: Dr Rituraj Purohit
Background: Methyltransferase
like 3 (METTL3) is an RNA methyltransferase implicated in mRNA biogenesis,
decay, and translation control through N6-methyladenosine
(m6A) modification.
Methods: To find
new treatment strategies for lung cancer and to elucidate the mechanism
underlying the phenomenon, we treated the human lung cancer cell lines A549 and
H1299 to investigate the effect of METTL3 on lung cancer.
Results: We
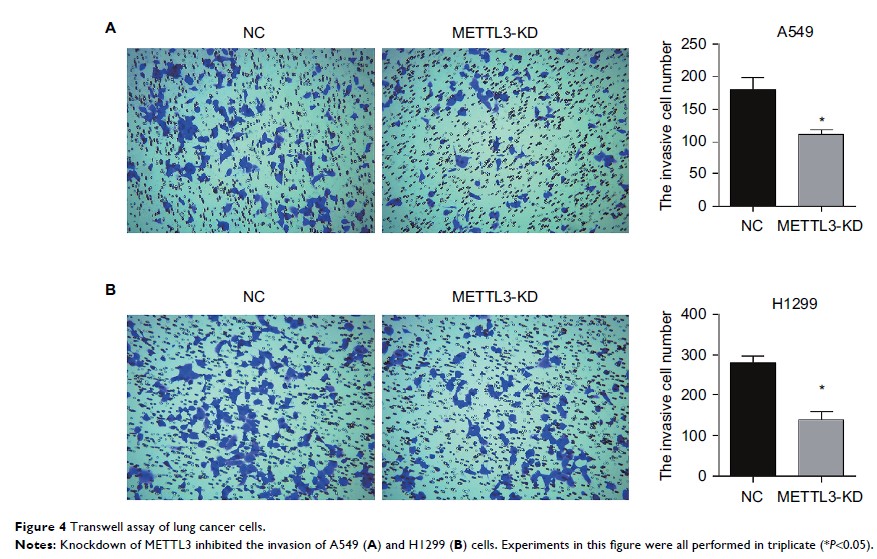
observed that knockdown of METTL3 inhibited the survival and proliferation of
A549 and H1299 cells. The migration and proliferation of both cell lines were
significantly decreased, and the apoptosis was induced in comparison with
control cells. These results were further confirmed by the transfection of
miRNA of METTL3 increased the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio in A549 and H1299 cells, which is
a sign that mitochondrial apoptotic pathway was triggered. The PI3K/Akt pathway
is implicated in cell growth and survival and we also observed that knockdown
of METTL3 changed the expression and phosphorylation of proteins of PI3K
signaling pathway members. Further, our results demonstrated that miR-600
inhibited the expression of METTL3 and reversed the positive effect of METTL3
on NSCLC progression, indicating an miR-600/METTL3 pathway in NSCLC.
Conclusion: These
data suggested that miR-600 inhibited lung cancer via down-regulating METTL3
expression, and knockdown of METTL3 might be used as a novel strategy for lung
cancer therapy.
Keywords: METTL3,
miRNA, lung cancer, A549, H1299, apoptosis, PI3K pathway