108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

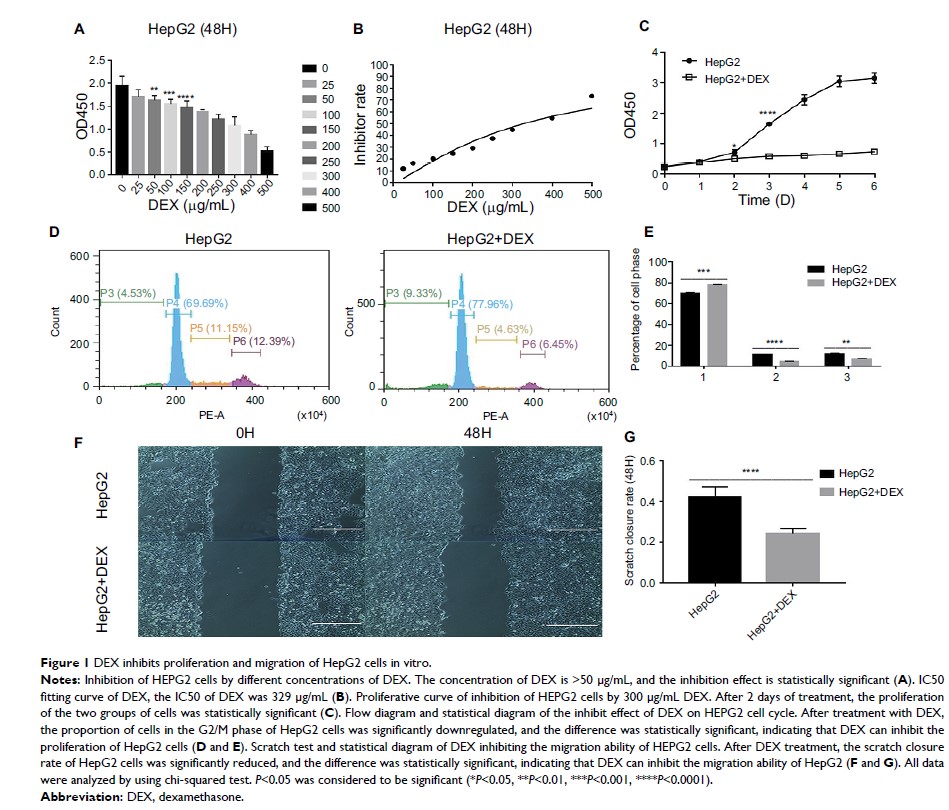
地塞米松抑制肿瘤细胞增殖
Authors Wu Y, Xia R, Dai C, Yan S, Xie T, Liu B, Gan L, Zhuang Z, Huang Q
Received 14 September 2018
Accepted for publication 12 December 2018
Published 1 February 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1141—1154
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S187659
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chien-Feng Li
Objective: Dexamethasone
(DEX) is a glucocorticoid that is commonly used in clinics. Previously, DEX has
been shown to inhibit the function of immune system; however, DEX is often used
to treat side reactions, such as nausea and vomiting caused by chemotherapy in
clinics. Therefore, it is necessary to study the role of DEX in the treatment
of cancer.
Methods: The effects
of DEX on HepG2 were studied in vitro by Cell Counting Kit-8 method, cell
cycle, and scratch test. The transplanted tumor model of HepG2 was established
in nude mice to study the anti-tumor effect of DEX in vivo. In addition, in
order to study the effect of DEX on the immune system, we also established a
transplanted tumor model of 4T1 in normal immunized mice to study treatment
effect and mechanism of DEX in mice of normal immune function.
Results: The
results showed that DEX inhibited the proliferation of HepG2 in vitro and in
vivo, affecting the cycle and migration of HepG2 cells, and the expression of
c-Myc and the activation of mTOR signaling pathway were inhibited. The
expression of key enzymes related to glucose metabolism is altered, especially
that of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase2 (PCK2). In normal immunized mice,
DEX also inhibits the proliferation of tumor cells 4T1, while the proportion of
CD4+CD45+T cells and CD8+CD45+ T cells in CD45+ cells in the lymph nodes
upregulated, the proportion of Treg cells in CD4+ T cells downregulated in
lymph nodes, and the proportion of MDSCs in tumor tissues downregulated.
Conclusion: DEX can
inhibit tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. The mechanism is to inhibit the
activation of mTOR signaling pathway by inhibiting the expression of c-Myc,
further affecting the expression of key enzymes involved in glucose metabolism,
especially PCK2.In addition, DEX has an inhibitory effect on the immune system,
which may be the reason why DEX still has anti-tumor effect in normal mice.
Keywords: dexamethasone,
glycolysis, Warburg effect, HepG2, 4T1, immune cells, immune system