109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

雷尼替丁 (Ranitidine) 通过重塑患有帕金森病 (Parkinson's disease) 的大鼠的神经化学变化缓解左旋多巴 (levodopa) 诱发的异动症
Authors Shi H, Yang X, Zhao H, Zhang S, Zu J, Zhang W, Shen X, Cui G, Hua F, Yan C
Published Date May 2015 Volume 2015:11 Pages 1331—1337
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S80174
Received 2 January 2015, Accepted 11 March 2015, Published 27 May 2015
Background: Levodopa
(L-dopa) remains the best drug in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease (PD).
Unfortunately, long-term L-dopa caused motor complications, one of which
is L-dopa-induced dyskinesia (LID). The precise mechanisms of LID are not
fully understood. We have previously reported that ranitidine could reduce LID
by inhibiting the activity of protein kinase A pathway in a rat model of PD. It
is demonstrated that neurotransmitters such as γ-aminobutyric-acid (GABA) and
glutamate (Glu) are also involved in the expression of LID. But whether
ranitidine could reduce LID by remodeling the neurochemical changes is unknown.
Methods: In the present study,
we produced PD rats by injection of 6-hydroxydopamine. Then PD rats were
treated with vehicle, L-dopa (6 mg/kg, plus benserazide
12 mg/kg, intraperitoneal [ip]) or L-dopa (6 mg/kg, plus
benserazide 12 mg/kg, ip) plus ranitidine (10 mg/kg, oral). Abnormal
voluntary movements were adopted to measure the antidyskinetic effect of
ranitidine in PD rats. Rotarod tests were used to observe whether ranitidine
treatment affects the antiparkinsonian effect of L-dopa. In vivo
microdialysis was used to measure nigral GABA and striatal Glu in PD rats.
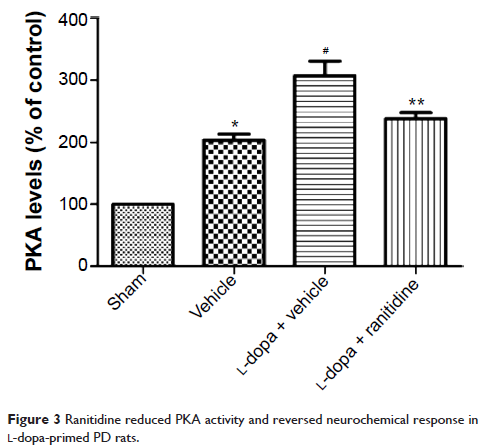
Results: We found that
ranitidine pretreatment reduced abnormal voluntary movements
in L-dopa-primed PD rats without affecting the antiparkinsonian effect
of L-dopa. In parallel with behavioral improvement, ranitidine
pretreatment reduced protein kinase A activity and suppressed the surge of
nigral GABA and striatal Glu.
Conclusion: These data
indicated that ranitidine could reduce LID by modeling neurochemical changes
induced by L-dopa, suggesting a novel mechanism of ranitidine in the
treatment of LID.
Keywords: ranitidine,
Parkinson’s disease, levodopa-induced dyskinesia, PKA, γ-aminobutyric-acid,
glutamate