108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

粘膜下浸润性结直肠癌淋巴结转移的病理危险因素
Authors Zhang Q, Wang L, Huang D, Xu M, Weng W, Ni S, Tan C, Sheng W
Received 28 July 2018
Accepted for publication 21 December 2018
Published 30 January 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 1107—1114
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S181740
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Rituraj Purohit
Background: Risk
grade assessment determines therapy in patients with submucosal invasive
colorectal carcinoma (CRC). However, treatment decisions are often difficult
due to a lack of consensus on which risk factors should be considered. We aimed
to identify predictive risk factors for lymph node metastasis (LNM) in a large
cohort of submucosal invasive CRC patients from China.
Patients and methods: Following
collection of clinicopathological data and disease-free survival (DFS) rates
from 290 patients who underwent radical intestinal resection with regional
lymphadenectomy, we immunohistochemically assessed expression of DNA mismatch
repair (MMR) proteins and p53. The correlation between clinicopathological
parameters, MMR expression, p53 status, and LNM status was determined using
chi-squared tests and logistic analysis. Receiver operator characteristic curve
analysis was used to compare the predictive values. The DFS curves were plotted
using the Kaplan–Meier method.
Results: LNM was
detected in 15.5% of the cases (45/290 patients). Three pathological
characteristics, high tumor differentiation grade, lymphovascular invasion
(LVI), and tumor budding, were all positively related to LNM in univariate and
multivariate analyses (P <0.05). MMR status did not correlate with either
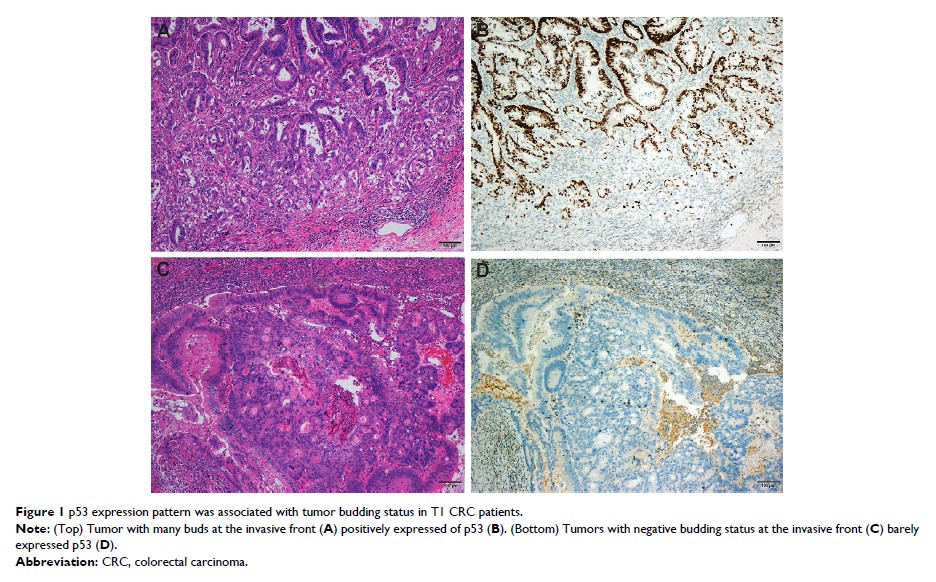
LNM or the pathological characteristics (P >0.05). Overexpression of p53 was associated with
tumor budding status (P =0.036). With a negative predicative value of 0.92
and area under the curve of 0.76 (95% CI: 0.68–0.85), the combination of these
three factors provided optimal predictive ability. Patients with all three risk
factors had poorer DFS (P <0.001).
Conclusion: High
tumor grade, LVI, and positive tumor budding serve as useful LNM predictors in
submucosal invasive CRC.
Keywords: CRC, LNM,
risk factor, MMR, p53