109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

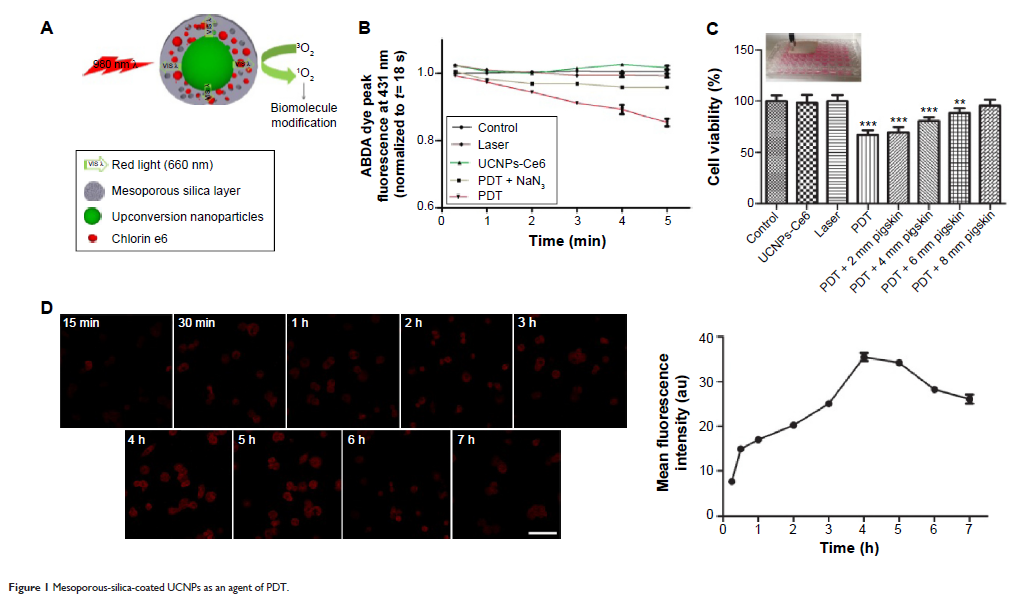
上转换纳米粒子介导的光动力疗法通过 ROS 突发和线粒体蛋白酶激活的方式诱导 THP-1 巨噬细胞凋亡
Authors Zhu X, Wang H, Zheng LB, Zhong ZY, Li XS, Zhao J, Kou JY, Jiang YQ, Zheng XF, Liu ZN, Li HX, Cao WW, Tian Y, Wang Y, Yang LM
Published Date May 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 3719—3736
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S82162
Received 7 February 2015, Accepted 7 April 2015, Published 22 May 2015
Abstract: Atherosclerosis (AS) is the most vital cardiovascular disease, which poses a
great threat to human health. Macrophages play an important role in the
progression of AS. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) has emerged as a useful
therapeutic modality not only in the treatment of cancer but also in the
treatment of AS. The purpose of this study was to determine the molecular
mechanisms underlying the activity of PDT, using mesoporous-silica-coated
upconversion fluorescent nanoparticles encapsulating chlorin e6 (UCNPs-Ce6) in
the induction of apoptosis in THP-1 macrophages. Here, we investigated the
ability of UCNPs-Ce6-mediated PDT to induce THP-1 macrophage apoptosis by
facilitating the induction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and regulation of
mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) to depolarize mitochondrial
membrane potential (MMP). Both Bax translocation and the release of cytochrome
C were examined using immunofluorescence and Western blotting. Our results
indicated that the levels of ROS were significantly increased in the PDT group,
resulting in both MPTP opening and MMP depolarization, which led to apoptosis.
In addition, immunofluorescence and Western blotting revealed that PDT induced
both Bax translocation and the release of cytochrome C, as well as upregulation
of cleaved caspase-9, cleaved caspase-3, and cleaved poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase. Therefore, we demonstrated that UCNPs-Ce6-mediated PDT induces
apoptosis in THP-1 macrophages via ROS bursts. The proapoptotic factor Bax
subsequently translocates from the cytosol to the mitochondria, resulting in
the MPTP opening and cytochrome C release. This study demonstrated the great
potential of UCNPs-Ce6-mediated PDT in the treatment of AS.
Keywords: atherosclerosis,
photodynamic therapy, fluorescent nanoparticles, reactive oxygen species,
apoptosis, macrophages