109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用自组装纳米颗粒进行黄芩素 (Baicalein) 和紫杉醇 (paclitaxel) 给药:在体外和体内的协同抗肿瘤效果
Authors Wang W, Xi M, Duan X, Wang Y, Kong F
Published Date May 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 3737—3750
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S80297
Received 4 January 2015, Accepted 18 February 2015, Published 22 May 2015
Purpose: Combination
anticancer therapy is promising to generate synergistic anticancer effects to
maximize the treatment effect and overcome multidrug resistance. The aim of the
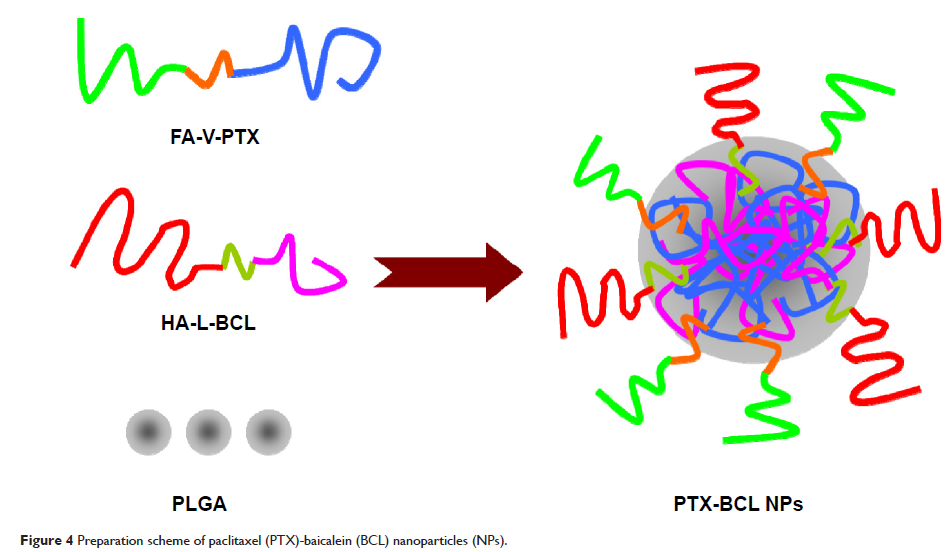
study reported here was to develop multifunctional, dual-ligand, modified,
self-assembled nanoparticles (NPs) for the combination delivery of baicalein
(BCL) and paclitaxel (PTX) prodrugs.
Methods: Prodrug of PTX and
prodrug of BCL, containing dual-targeted ligands of folate (FA) and hyaluronic
acid (HA), were synthesized. Multifunctional self-assembled NPs for combination
delivery of PTX prodrug and BCL prodrug (PTX-BCL) were prepared and the synergistic
antitumor effect was evaluated in vitro and in vivo. The in vitro transfection
efficiency of the novel modified vectors was evaluated in human lung cancer
A549 cells and drug-resistant lung cancer A549/PTX cells. The in vivo antitumor
efficiency and systemic toxicity of different formulations were further
investigated in mice bearing A549/PTX drug-resistant human lung cancer
xenografts.
Results: The size of the
PTX-BCL NPs was approximately 90 nm, with a positive zeta potential
of +3.3. The PTX-BCL NPs displayed remarkably better antitumor activity
over a wide range of drug concentrations, and showed an obvious synergism
effect with CI50 values of 0.707 and 0.513, indicating that
double-ligand modification and the co-delivery of PTX and BCL prodrugs with
self-assembled NPs had remarkable superiority over other formulations.
Conclusion: The prepared
PTX-BCL NP drug-delivery system was proven efficient by its targeting of
drug-resistant human lung cancer cells and delivering of BCL and PTX prodrugs.
Enhanced synergistic anticancer effects were achieved by PTX-BCL NPs, and
multidrug resistance of PTX was overcome by this promising targeted
nanomedicine.
Keywords: combination
chemotherapy, prodrug-based nano-drug delivery system, multidrug resistance,
self-assembled nanoparticles