109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

成纤维细胞生长因子受体 4 对非小细胞肺癌 (NSCLC) 的预后意义
Authors Huang H, Feng H, Qiao H, Ren Z, Zhu G
Published Date May 2015 Volume 2015:8 Pages 1157—1164
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S81659
Received 27 January 2015, Accepted 11 March 2015, Published 22 May 2015
Background: Fibroblast
growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) has been proved to be correlated with
progression and prognosis in many cancers. However, the significance of FGFR4
in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is still not well elucidated.
Methods: In our experiment, we
detected FGFR4 expression in 237 samples of NSCLC with immunohistochemistry,
and further analyzed the correlation between FGFR4 and clinicopathologic
features of NSCLC with chi-square test. Moreover, we evaluated the prognostic
value of FGFR4 by Kaplan–Meier survival curve and Cox regression model. By
regulating the expression of FGFR4 by overexpression or knockdown, we assessed
the role of FGFR4 on NSCLC cell proliferation.
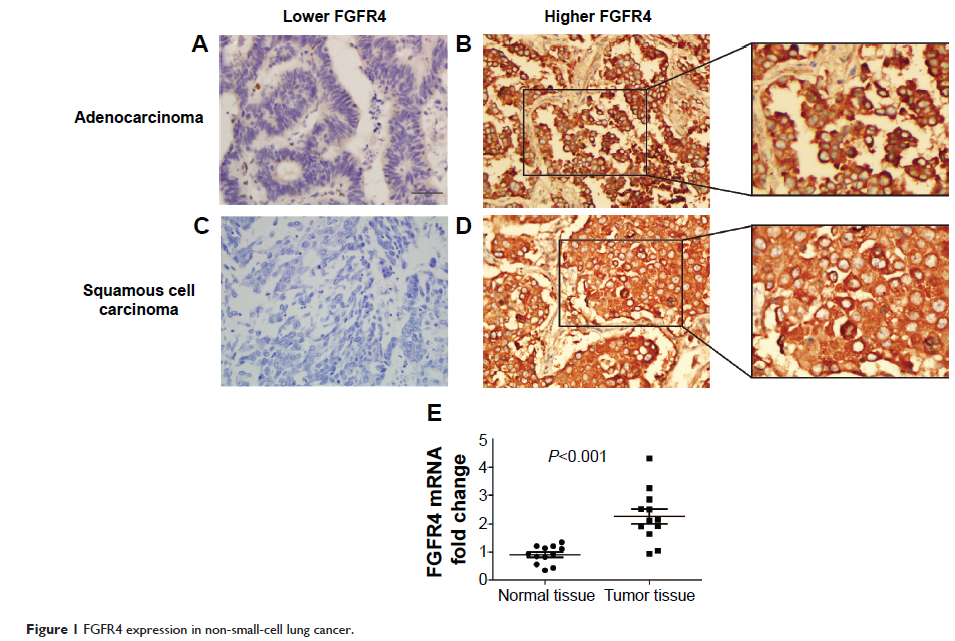
Results: FGFR4 expression was
high in NSCLC (46.8%, 111/237). FGFR4 expression was significantly associated
with tumor diameter (P =0.039). With
univariate (P =0.009) and multivariate (P =0.002) analysis, FGFR4 was
identified as an independent prognostic factor in NSCLC (P =0.009). Moreover, FGFR4 can
promote the proliferation of NSCLC cell lines.
Conclusion: FGFR4 is an
independent prognostic biomarker in NSCLC. FGFR4 can accelerate the
proliferation of NSCLC cell lines, indicating FGFR4 could be a potential drug
target of NSCLC.
Keywords: fibroblast growth
factor 4, non-small-cell lung cancer, prognosis, proliferation