108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

一种多功能靶向纳米剂用于对卵巢癌细胞进行双模态影像引导治疗的效果
Authors Chen C, Sun J, Chen S, Liu Y, Zhu S, Wang Z, Chang S
Received 20 September 2018
Accepted for publication 1 December 2018
Published 21 January 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 753—769
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S187929
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Purpose: Nanomedicine
has emerged as a novel therapeutic modality for cancer treatment and diagnosis.
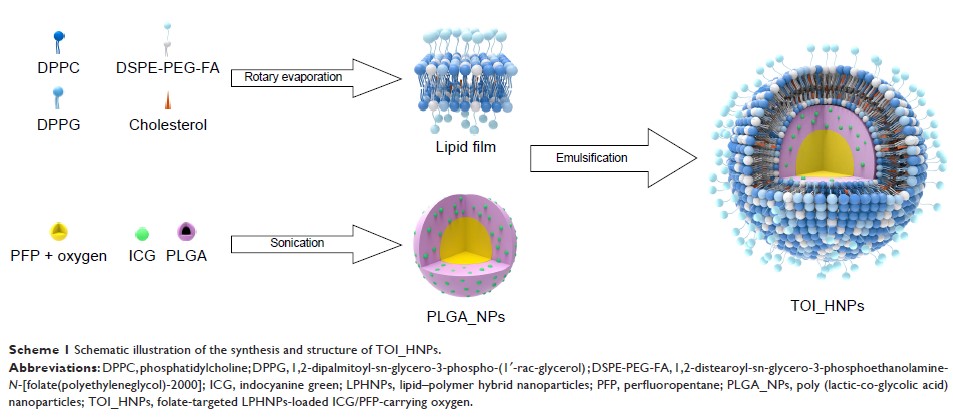
Lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles (LPHNPs) are core–shell nanoparticle (NP)
structures comprising polymer cores and lipid shells, which exhibit
complementary characteristics of both polymeric NPs and liposomes. However, it
is difficult to wrap perfluoropentane (PFP) into core–shell NPs in the existing
preparation process, which limits its application in the integration of
diagnosis and treatment.
Methods: The
folate-targeted LPHNPs-loaded indocyanine green/PFP-carrying oxygen (TOI_HNPs)
using a combination of two-step method and solution evaporation technique for
the first time. The essential properties and dual-mode imaging characteristics
of developed NPs were determined. The cellular uptake of TOI_HNPs was detected
by confocal microscopy and flow cytometry. The SKOV3 cell viability and
apoptosis rate were evaluated by 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2-H-tetrazolium
bromide (MTT) assay and flow cytometry. The ROS was demonstrated by
fluorescence microplate reader and the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor
1-alpha (HIF-1α) and IL-6 was detected by Western blot.
Results: TOI_HNPs
showed spherical morphology with particle size about (166.83±5.54) nm and zeta
potential at -(30.57±1.36) mV. It exhibited better stability than lipid NPs and
higher encapsulation efficiency as well as active targeting ability than poly
(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) NPs. In addition, the novel NPs could also act
as the contrast agents for ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging, providing
precision guidance and monitoring. Furthermore, TOI_HNPs-mediated
photo–sonodynamic therapy (PSDT) caused more serious cell damage and more
obvious cell apoptosis, compared with other groups. The PSDT mediated by
TOI_HNPs induced generation of intracellular ROS and downregulated the
expression of HIF-1α and IL-6 in SKOV3 cells.
Conclusion: This kind
of multifunctional-targeted nanoagent may provide an ideal strategy for
combination of high therapeutic efficacy and dual-mode imaging guidance.
Keywords: core-shell
nanoparticle, phase transformation, photoacoustic imaging, laser, ultasound,
photo-sonodynamic therapy