108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

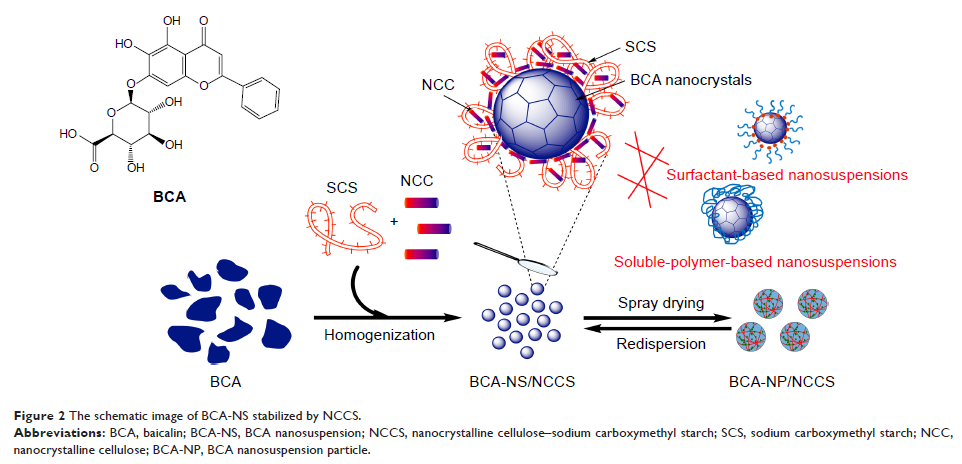
复合纳米晶微纤维素 - 羧甲基淀粉钠可使新型可再分散纳米悬浮液变得稳定,以增强黄芩苷的溶出度和口服生物利用度
Authors Xie J, Luo Y, Liu Y, Ma Y, Yue P, Yang M
Received 17 August 2018
Accepted for publication 6 November 2018
Published 3 January 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 353—369
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S184374
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: To
improve the dissolution and bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs, novel
nanosuspensions using co-processed nanocrystalline cellulose–sodium
carboxymethyl starch (NCCS) as a synergetic stabilizer were first designed.
Methods: Co-processed
NCCS was prepared by means of homogenization. Poorly soluble baicalin (BCA) was
used as a model drug. BCA nanosuspension (BCA-NS/NCCS) using co-processed NCCS
as a dispersant was prepared via homogenization and further converted into the
dried BCA nanosuspension particle (BCA-NP/NCCS) via spray drying. The influence
of NCCS on the dispersion efficiency of BCA-NS/NCCS was investigated.
Morphology and crystal characteristic of NCCS and BCA-NP were analyzed. The
dissolution and bioavailability evaluation were performed to investigate the
feasibility of NCCS as a stabilizer for BCA-NS/NCCS and BCA-NP.
Results: The
optimum 50% concentration of NCCS (nanocrystalline cellulose [NCC]:sodium carboxymethyl
starch [SCS]=60:40) could be mostly beneficial for formation and stability of
BCA-NS/NCCS. NCCS could completely prevent aggregation of BCA-NP during spray
drying and enhance the redispersibility as well as dissolution of spray-dried
BCA-NP, which might be attributed to “brick–concrete”-based barrier effect of
NCCS and the swelling capacity of superdisintegrant SCS. The crystal state of
NCC and BCA presented in BCA-NP/NCCS remained unchanged during the
homogenization. The BCA-NP/NCCS exhibited a fast dissolution rate and
significantly enhanced bioavailability of BCA. The AUC(0–∞) of the
BCA-NP/NCCS (8,773.38±718.18 µg/L·h) was 2.01 times (P <0.05) as high
as that of the crude BCA (4,354.61±451.28 µg/L·h).
Conclusion: This
study demonstrated that novel surfactant-free nanosuspensions could be prepared
using co-processed NCCS as a synergetic stabilizer and also provided a feasible
strategy to improve the dissolution and oral bioavailability of poorly soluble
drug.
Keywords: nanocrystalline
cellulose, Pickering nanosuspensions, nanocrystals, solid particles stabilizer,
oral bioavailability