108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-211 的 rs187960998 多态性通过 CHD5 中的 3'UTR 下调来预防人结肠癌的发生
Authors Zhu L, Wang R, Zhang L, Zuo C, Zhang R, Zhao S
Received 20 July 2018
Accepted for publication 16 November 2018
Published 3 January 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 405—412
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S180935
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Background: Previous
research indicated that overexpression of miRNA-211 could promote colorectal cancer
cell growth by targeting tumor suppressive gene
Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 5 (CHD5) in human colon cancer (CC).
Moreover, the function of the single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) located in
the mature region of miR-211 has not been investigated. In this study, we found
that SNP of rs187960998 in miR-211 was involved in the occurrence of CC by
acting as a tumor suppressor by mal-regulation of its target gene CHD5 .
Materials and methods: The
genotype of total 685 CC patients was detected by real-time PCR, the
proliferation of CC cell lines with different genotypes of miR-211 was
determined by Cell Counting Kit-8, cell invasion evaluated by transwell and the
activity of the CHD5 promoter in CC cell lines transfected with different
miR-211 was determined by luciferase assay. The expression of CHD5 in CC
patients was determined by the immunohistochemistry, and the relapse-free
survival rate was analyzed by Kaplan–Meier analysis.
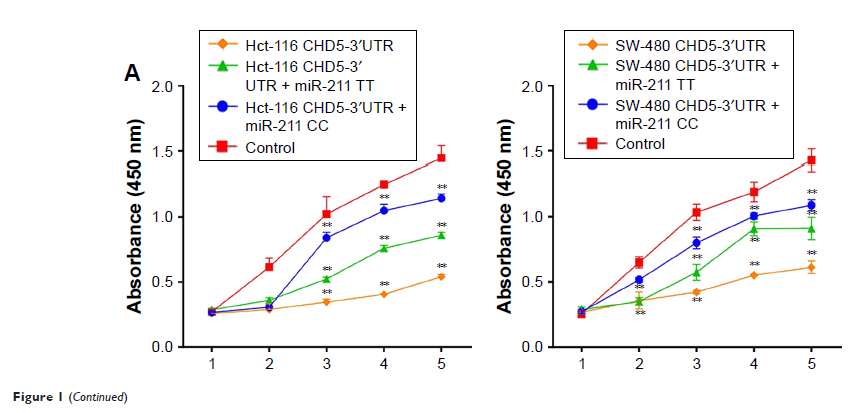
Results: C/T SNP
of miR-211 could inhibit CC cell proliferation and invasion by upregulation of
CHD5. And SNP in rs187960998 of miR-211 was associated with tumor size,
metastasis and tumor differentiation in CC patients. Patients with CC genotype
have significantly low CHD5 expression than the T-carrier, while no significant
expression difference in miR-211 expression among different genotype subsets.
Patients with CC genotype have significantly shorter postsurgery survival rate
compared to the T-carrier.
Conclusion: rs187960998 in
miR-211 was highly associated with a decreased risk of CC in the Chinese
population by deregulating a tumor suppressive gene CHD5.
Keywords: miR-211, colon
cancer, CHD5, SNP, survival