109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

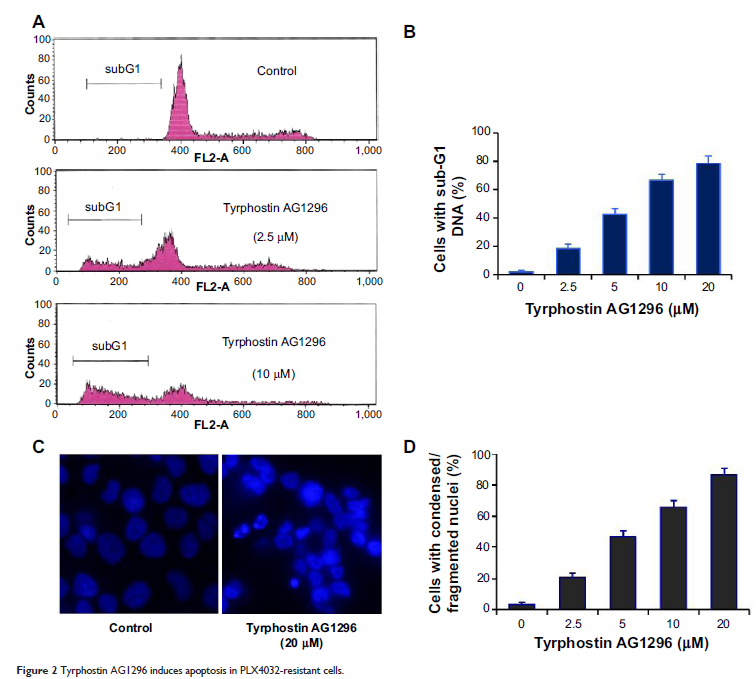
酪氨酸磷酸化抑制剂 AG1296,一种血小板衍生生长因子受体抑制剂,能诱导耐 PLX4032 黑色素瘤细胞的细胞凋亡,并降低其生存与迁移能力
Authors Li Y, Li Y, Liu Q, Wang A
Published Date May 2015 Volume 2015:8 Pages 1043—1051
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S70691
Received 6 July 2014, Accepted 24 September 2014, Published 14 May 2015
Abstract: Melanoma is
the deadliest form of skin cancer, and BRAFV600E is a driver mutation that
promotes melanoma growth and survival. PLX4032 is the first effective compound
in clinical use for the treatment of patients with mutant BRAFV600. However,
resistance to PLX4032 develops quickly within months. Activation of a series of
receptor tyrosine kinases, including the platelet-derived growth factor
receptor (PDGFR), has been identified to be the underlying mechanism for
development of resistance to PLX4032. In this work, we investigated the
anticancer activity of tyrphostin AG1296, a PDGFR inhibitor, in melanoma,
especially PLX4032-resistant melanoma. We found that tyrphostin AG1296 could
effectively reduce the viability of both PLX4032-sensitive and PLX4032-resistant
melanoma cells. There is an additive effect between tyrphostin AG1296 and
PLX4032 in reducing cell viability. Tyrphostin AG1296 induced dramatic
apoptosis in PLX4032-resistant cells, and also dramatically inhibited migration
of PLX4032-resistant cells. Importantly, tyrphostin AG1296 significantly
suppressed A375R tumor growth in vivo. This is the first report on the
anticancer activity of tyrphostin AG1296 in melanoma. Tyrphostin AG1296 is a
promising compound in the treatment of melanoma, especially for those who have
developed resistance towards BRAF inhibitors, and might shed new light on
melanoma therapy.
Keywords: melanoma, PLX4032,
resistance, viability, apoptosis, migration