109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
针对上皮细胞粘附分子 (Ep-CAM ) 基因的干扰载体构建及其对结肠直肠癌细胞增殖的影响
Authors Qi Y, Zhou F, Zhang L, Liu L, Xu H, Guo H
Published Date May 2015 Volume 2015:9 Pages 2647—2652
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S82917
Received 15 February 2015, Accepted 10 March 2015, Published 14 May 2015
Background: Prior study indicates that abnormal protein expression and functional
changes in the development and progression of colorectal cancer is related to
gene expression. The aim of this study was to construct an interference plasmid
targeting the Ep-CAM gene and to investigate its
effects on the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells.
Methods: In this study, HT-29 and HCT-116 colorectal cancer cell lines were selected as cell models. The double-stranded micro (mi)RNA oligo was inserted into the pcDNATM6.2-GW/EmGFPmiR vector, which is an expression of miRNA. Lipofectamine™ 2000 was used to transfer plasmid into the empty plasmid group (transfected pcDNATM6.2-GW/EmGFPmiR-neg) and the interference group (transfected pcDNATM6.2-GW/EmGFPmiR-Ep-CAM-1), respectively. Meanwhile, the nontransferred HT-29 and HCT-116 acts as the blank control group. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was used to detect the transfection efficiency. Western blot was used to detect Ep-CAM protein expression. The cell proliferation in each group was detected by using 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay.
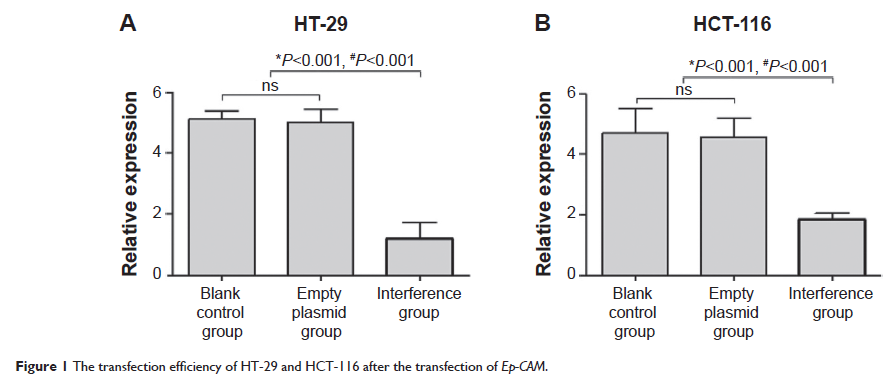
Results: The results indicated that the Ep-CAM messenger (m)RNA expression in the interference group was lower significantly compared with that of the empty plasmid group and control group (P <0.01). Western blot analysis results showed that Ep-CAM protein expression was significantly lower in interference group compared with that of the empty plasmid group and the control group (P <0.01). MTT assay results demonstrated that the proliferation ability of cells in the interference group was significantly inhibited compared with the two other groups (P <0.05).
Conclusion: Silencing of Ep-CAM can significantly inhibit the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells.
Keywords: epidermal growth factor, Ep-CAM, colorectal cancer, vector construction
Methods: In this study, HT-29 and HCT-116 colorectal cancer cell lines were selected as cell models. The double-stranded micro (mi)RNA oligo was inserted into the pcDNATM6.2-GW/EmGFPmiR vector, which is an expression of miRNA. Lipofectamine™ 2000 was used to transfer plasmid into the empty plasmid group (transfected pcDNATM6.2-GW/EmGFPmiR-neg) and the interference group (transfected pcDNATM6.2-GW/EmGFPmiR-Ep-CAM-1), respectively. Meanwhile, the nontransferred HT-29 and HCT-116 acts as the blank control group. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was used to detect the transfection efficiency. Western blot was used to detect Ep-CAM protein expression. The cell proliferation in each group was detected by using 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay.
Results: The results indicated that the Ep-CAM messenger (m)RNA expression in the interference group was lower significantly compared with that of the empty plasmid group and control group (P <0.01). Western blot analysis results showed that Ep-CAM protein expression was significantly lower in interference group compared with that of the empty plasmid group and the control group (P <0.01). MTT assay results demonstrated that the proliferation ability of cells in the interference group was significantly inhibited compared with the two other groups (P <0.05).
Conclusion: Silencing of Ep-CAM can significantly inhibit the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells.
Keywords: epidermal growth factor, Ep-CAM, colorectal cancer, vector construction