109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国眼内压患者的固定联合治疗——集中于比马前列素-噻吗洛尔 (Bimatoprost-timolol)
Authors Fang Y, Ling Z, Sun X
Published Date May 2015 Volume 2015:9 Pages 2617—2625
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S80338
Received 5 January 2015, Accepted 26 February 2015, Published 13 May 2015
Abstract: Glaucoma is
a common eye disease that can lead to irreversible vision loss if left
untreated. The early diagnosis and treatment of primary open-angle glaucoma is
challenging, and visual impairment in Chinese glaucoma patients is a serious
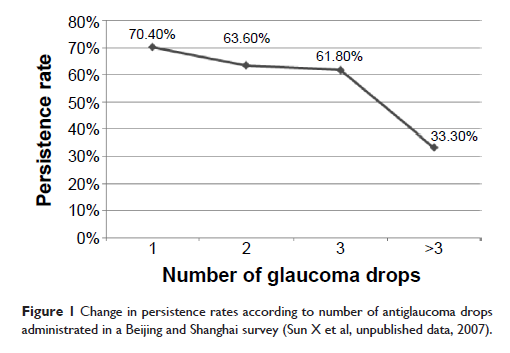
concern. Most of these patients need more than one topical antiglaucoma agent
to control their intraocular pressures (IOPs). In the People’s Republic of
China, the daily cost of different glaucoma medication varies greatly, and the
treatment habits differ throughout the country. Prostaglandin analogs (PGAs)
are recommended as first-line monotherapy, because of their efficacy and low
risk of systemic side effects. Fixed-combination drops, particularly PGA-based
fixed combinations, have recently been developed and used in patients with
progression or who have failed to achieve their target IOPs. Here, we reviewed
the current literature on the use of bimatoprost-timolol fixed combination
(BTFC) in the People’s Republic of China. BTFC has achieved good efficacy and
tolerability in Chinese clinical trials. In addition, BTFC is more cost
effective compared with other fixed combinations available in the People’s
Republic of China. Fixed-combination drops may offer benefits, such as keeping
the ocular surface healthy, convenience of administration, and improvement in
long-term adherence and quality of life. Therefore, BTFC has great potential
for the treatment of Chinese glaucoma patients. However, the long-term efficacy
of BTFC, comparisons of BTFC with other fixed-combination drugs, and treatment
adherence and persistence with treatment in Chinese patients are unknown and
will require further study.
Keywords: glaucoma, open-angle,
bimatoprost