108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MicroRNA-302a-3p 通过遏制增殖和侵袭来抑制肝细胞癌的进展
Authors Ye Y, Song Y, Zhuang J, Wang G, Ni J, Zhang S, Xia W
Received 3 March 2018
Accepted for publication 23 May 2018
Published 10 December 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 8175—8184
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S167162
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Background: Involvement of
microRNAs in tumor development and their potential as prognostic biomarkers had
been well acknowledged. However, the expression, clinical significance, and
functional mechanisms of microRNA (miR)-302a-3p in hepatocellular carcinoma
(HCC) have not been reported.
Patients and methods: Real-time
quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used to evaluate the expression of
miR-302a-3p in 111 HCC tissues and adjacent normal liver tissues. Its
association with clinicopathological characteristics was analyzed by the
chi-square test. The Kaplan–Meier univariate survival analysis and multivariate
Cox regression analysis were used to identify the clinical significance of
miR-302a-3p in the overall survival (OS) of HCC patients. Transfection of
miR-302a-3p mimics into HepG2 and Huh7 HCC cell lines was conducted to reveal
its underlying mechanism in regulating HCC progression.
Results: miR-302a-3p
expression was significantly decreased in HCC tissues compared with that in
paired adjacent normal liver tissues (P =0.005). miR-302a-3p expression was correlated with
tumor number (P =0.003),
tumor size (P <0.001),
and tumor TNM stage (P =0.028). The Kaplan–Meier survival analysis showed
that patients in the high miR-302a-3p expression group had a better OS than
those in the low miR-302a-3p expression group (P =0.002).
Multivariate analysis confirmed that miR-302a-3p expression can be used as an
independent predictor for HCC prognosis (HR=0.480, 95% CI=0.249–0.894, P =0.039).
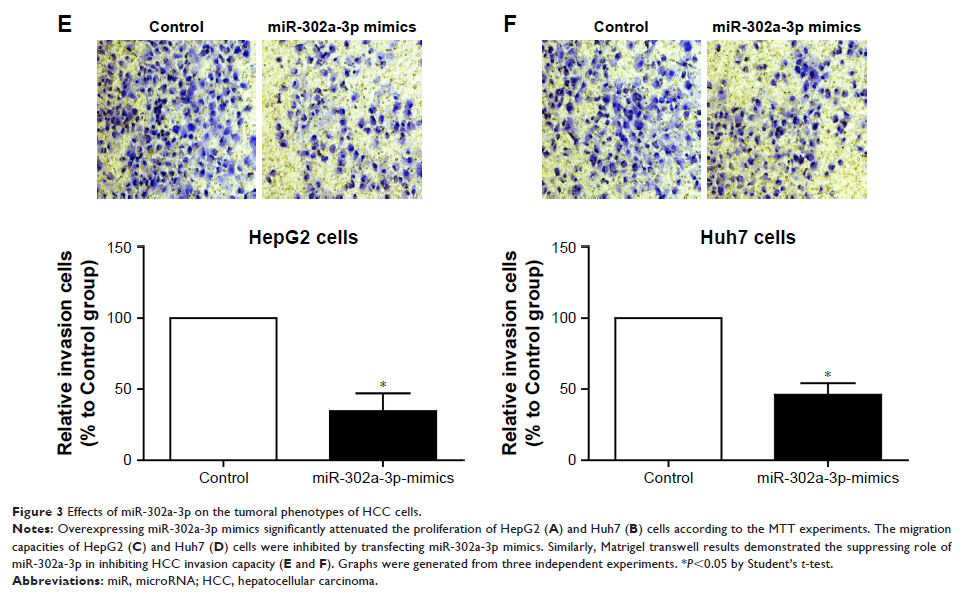
Proliferation, migration, and invasion capacities were all decreased in cells
transfected with miR-302a-3p mimics. Moreover, our data showed a direct effect
of miR302a-3p on inhibiting the expression and signaling of PRKACB in HCC
cells.
Conclusions: miR-302a-3p
serves as a tumor suppressor in HCC progression by directly inhibiting tumor proliferation
and invasion, and its low expression is a potential biomarker for predicting a
poor prognosis of HCC patients.
Keywords: hepatocellular
carcinoma, miR-302a-3p, invasion, prognosis, proliferation