109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
中国人群中 GSTM1 空白基因型与胃癌的风险: 一个更新的综合分析和回顾
Authors Zhang XL, Cui YH
Published Date April 2015 Volume 2015:8 Pages 969—975
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S79099
Received 11 December 2014, Accepted 2 March 2015, Published 28 April 2015
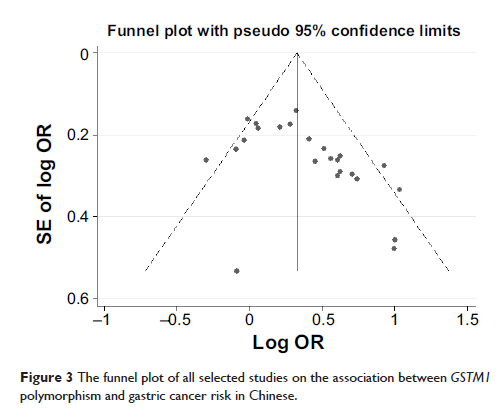
Abstract: Although a number of studies have been conducted on the association
between the GSTM1 null genotype and gastric
cancer in People’s Republic of China, this association remains elusive and
controversial. To clarify the effects of the GSTM1 null
genotype on the risk of gastric cancer, an updated meta-analysis was performed
in the Chinese population. Related studies were identified from PubMed,
Springer Link, Ovid, Chinese Wanfang Data Knowledge Service Platform, Chinese
National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), and Chinese Biology Medicine (CBM) up
to November 5, 2014. A total of 25 studies including 3,491 cases and 5,921
controls were included in this meta-analysis. Overall, a significant
association (odds ratio [OR] =1.47, 95% CI: 1.28–1.69) was found between
the null GSTM1 and gastric cancer risk when
all studies in Chinese population were pooled into the meta-analysis. In
subgroup analyses stratified by quality score, geographic area, and source of
controls, the same results were observed. Additionally, a significant
association was found both in smokers and non-smokers. This meta-analysis showed
that the null GSTM1 may be a potential biomarker
for gastric cancer risk in Chinese, and further studies with gene–gene and
gene–environment interactions are required for definite conclusions.
Keywords: meta-analysis, GSTM1 , polymorphism, gastric cancer
Keywords: meta-analysis, GSTM1 , polymorphism, gastric cancer