108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

利鲁唑通过突触后 GluR2 受体诱导脊髓疼痛信号 LTD
Authors Zhang X, Gao Y, Wang Q, Du S, He X, Gu N, Lu Y
Received 29 March 2018
Accepted for publication 27 June 2018
Published 26 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 2577—2586
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S169686
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr E Alfonso Romero-Sandoval
Purpose: Riluzole – a major therapeutic medicine for patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis – reportedly has anti-nociceptive and anti-allodynic efficacies in neuropathic pain models. However, little is known about its effect on neurotransmission in the spinal superficial dorsal horn (SDH). The present study aims to investigate the effects of riluzole on the synaptic transmission of SDH nociceptive pathways in both physiological and pathological conditions.
Materials and methods: Spinal nerve ligation was used to produce a neuropathic pain model. Mechanical allodynia behavior was assessed with Von Frey filaments. Riluzole’s effects on nociceptive synaptic transmission under both physiological and pathological conditions were examined by patch-clamp recordings in rat SDH neurons.
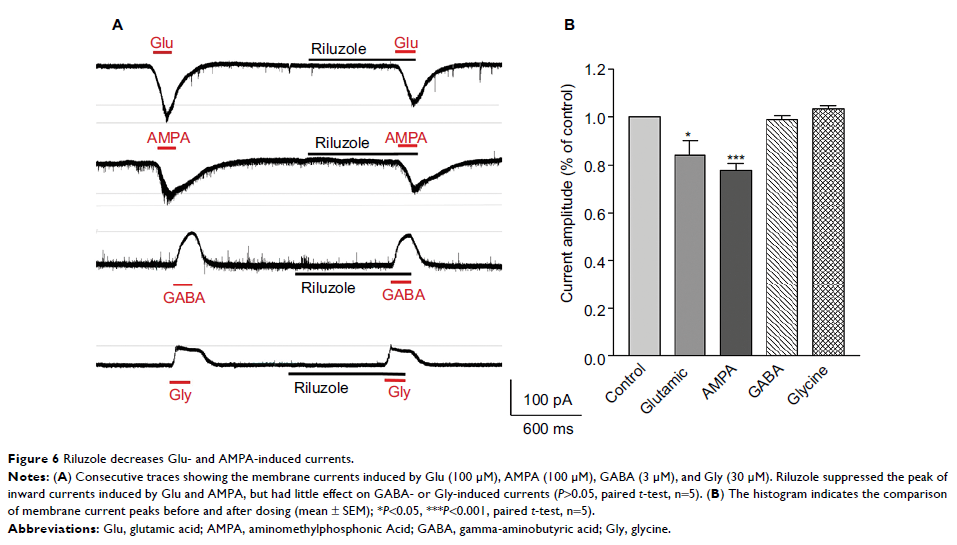
Results: The principal findings of the present study are three-fold. First, we affirm that riluzole has a remarkable long-lasting analgesic effect on both in vitro and in vivo pathological pain models. Second, the prolonged inhibitory effects of riluzole on spinal nociceptive signaling are mediated by both presynaptic and postsynaptic mechanisms. Finally, endocytosis of postsynaptic GluR2 contributes to the riluzole-induced long-term depression (LTD) of the spinal nociceptive pathway.
Conclusion: The present study finds that riluzole induces LTD of nociceptive signaling in the SDH and produces long-lasting anti-allodynia effects in nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain conditions via postsynaptic AMPA receptors associated with the endocytosis of GluR2.
Keywords: riluzole, neuropathic pain, superficial dorsal horn, SSDH, long-term depression, LTD, AMPA receptor endocytosis