108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

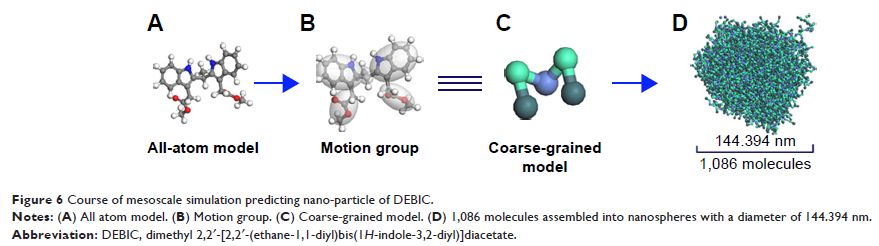
二甲基 2,2′-[2,2′-(乙烷-1,1-基) 双(1H -吲哚-3, 2-基) 双乙酸盐(Dimethyl 2,2′-[2,2′-(ethane-1,1-diyl)bis(1H-indole-3,2-diyl)]-diacetate):一种可用于纳米级组装的小分子,可抑制静脉血栓形成,并且不会引起出血副作用
Authors Wang Y, Chen H, Zhang X, Gui L, Wu J, Feng Q, Peng S, Zhao M
Received 29 June 2018
Accepted for publication 11 October 2018
Published 22 November 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 7835—7844
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S178683
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Background: Due to
the discovery that deep venous thrombosis (DVT) inhibitor is of
chemotherapeutic importance, the nano-property of dimethyl 2,2'-[2,2'-(ethane-1,1-diyl)bis(1H -indole-3,2-diyl)]-diacetate
(DEBIC), a recently reported antitumor agent, is worthy of characterization.
Materials and methods: One-pot
reaction was used to prepare DEBIC. Electrospray Ionization (+/-)-Fourier
Transform-Ion Cyclotron Resonance-Mass Spectrometer (ESI(+/-)-FT-ICR-MS),
quadrupole Collision Induced Dissociation (qCID) and nuclear overhauser effect
spectroscopy spectra were used to present the assembly of DEBIC. Transmission
electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy and
Faraday–Tyndall effect were used to visualize the nano-property of DEBIC. Rat
models were used to evaluate DVT inhibition and the bleeding reaction of DEBIC.
Results: One-pot
reaction can provide DEBIC in acceptable yield and high purity. In water, rat
plasma and lyophilized powders of DEBIC existed as particles of small
nano-size. In vivo DEBIC inhibited DVT in a dose-dependent manner. The minimal
effective dose of DEBIC was 1.7 µmol/kg. Even the dose of 36 µmol/kg/day DEBIC
did not induce bleeding side effect in DVT rats like in warfarin (0.82
µmol/kg/day).
Conclusion: DEBIC is
a small molecule capable of nano-scale assembly, inhibiting venous thrombosis
and inducing no bleeding side effect.
Keywords:
nano-property, DVT inhibition, bleeding-reaction, tumor, thrombosis