108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

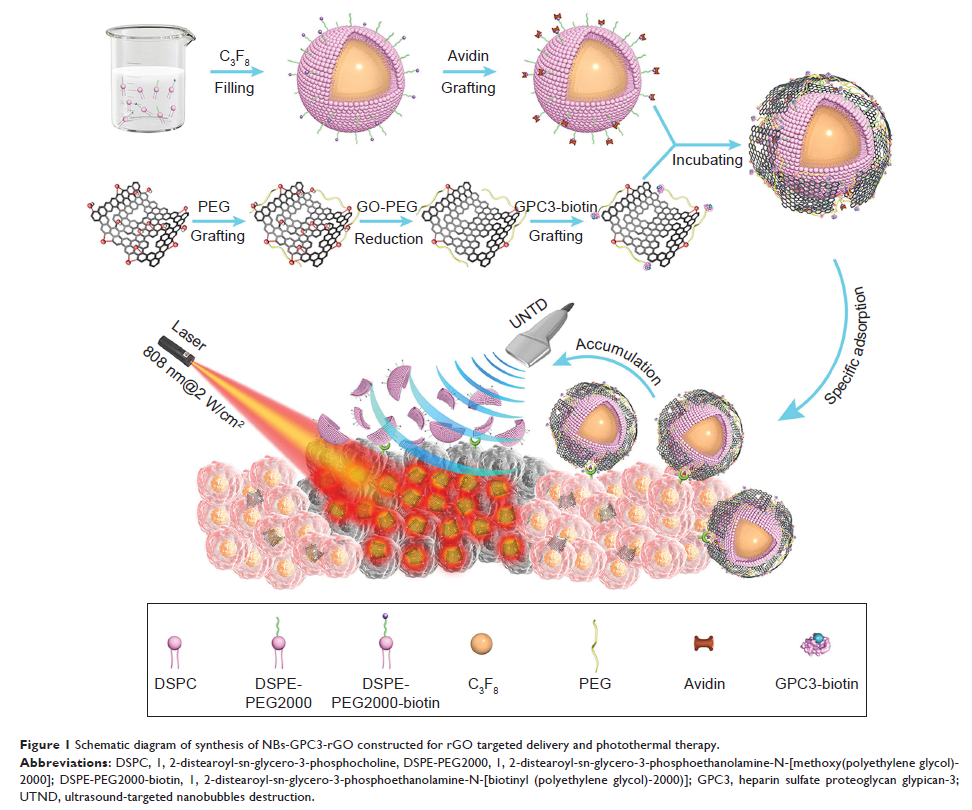
使用多功能超声纳米气泡靶向递送还原氧化石墨烯纳米片,用于可视化和增强的光热疗法
Authors Liu Z, Zhang J, Tian Y, Zhang L, Han X, Wang Q, Cheng W
Received 24 July 2018
Accepted for publication 23 September 2018
Published 22 November 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 7859—7872
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S181268
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Ultrasound
molecular imaging as a promising strategy, which involved the use of
molecularly targeted contrast agents, combined the advantages of
contrast-enhanced ultrasound with the photothermal effect of reduced graphene
oxide (rGO).
Methods and results: The
heparin sulfate proteoglycan glypican-3 (GPC3) is a potential molecular target
for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In this study, we covalently linked
biotinylated GPC3 antibody to PEGylated nano-rGO to obtain GPC3-modified
rGO-PEG (rGO-GPC3), and then combined rGO-GPC3 with avidinylated nanobubbles
(NBs) using biotin-avidin system to prepare NBs-GPC3-rGO with photothermal
effect and dispersibility, solubility in physiological environment. The average
size of NBs-GPC3-rGO complex was 700.4±52.9 nm due to the polymerization of
biotin-avidin system. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) showed NBs-GPC3-rGO
attached to human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cell. The ultrasound-targeted
nanobubble destruction (UTND) technology make use of the physical energy of
ultrasound exposure for the improvement of rGO delivery. Compared with other
control groups, the highest nanobubble destruction efficiency of NBs-GPC3-rGO
was attributed to the dissection effect of rGO on UTND. This is a positive
feedback effect that leads to an increase in the concentration of rGO around
the HepG2 cell. So NBs-GPC3-rGO using UTND and near-infrared (NIR) irradiation
resulted in cell viability within 24 h, 48 h, 72 h lower than other treatment
groups.
Conclusion: This work
established NBs-GPC3-rGO as an ultrasonic photothermal agent due to its
suitable size, imaging capability, photothermal efficiency for visual
photothermal therapy in vitro.
Keywords: reduced
graphene oxide, ultrasound-targeted nanobubble destruction, glypican-3, HepG2
cell, photothermal therapy