109669
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

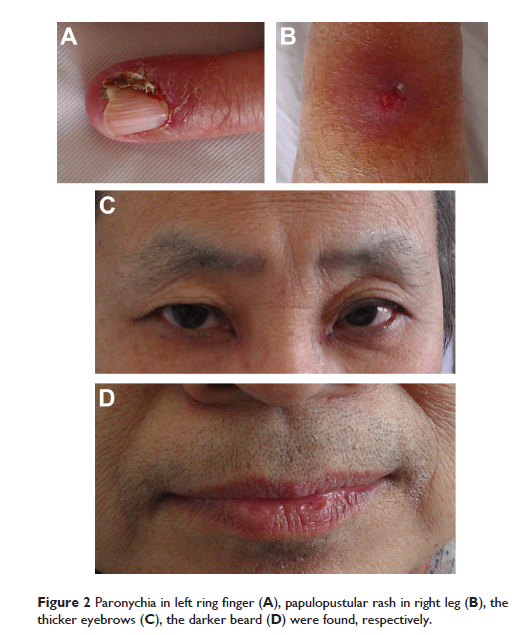
来自厄洛替尼 (Erlotinib) 的一系列的皮肤毒性,可以是非小细胞肺癌 (NSCLC) 治疗中的一个强有力的临床标记物: 病例报告和文献回顾
Authors Jin F, Zhu H, Kong L, Yu JM
Published Date April 2015 Volume 2015:8 Pages 943—946
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S83888
Received 3 March 2015, Accepted 1 April 2015, Published 23 April 2015
Abstract: Some
literature suggests that an EGFR inhibition-induced rash can be used as a
clinical marker, but few studies report the correlation between a spectrum of
cutaneous toxicities from EGFR inhibition and drug efficacy. We report about a
woman with a stage IV lung adenocarcinoma using erlotinib monotherapy, who
experienced a spectrum of cutaneous toxicities, including papulopustular rash,
mucositis, pruritus, xerosis, paronychia, and facial hirsutism. With treatment,
her metastatic lesions shrunk remarkably. This report suggests that some
non-small-cell lung cancer patients experiencing a spectrum of cutaneous
toxicities might have a good tumor response using erlotinib monotherapy. Our
findings may provide a method for clinicians to predict erlotinib efficacy in
non-small-cell lung cancer therapy without knowledge of the EGFR mutation status.
Keywords: cutaneous toxicity,
epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition, erlotinib, clinical marker,
non-small-cell lung cancer