108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

利用下一代小 RNA 测序检测 Smad4 阳性和 Smad4 阴性 SW620 人结肠癌细胞中的 miRNA 表达谱
Authors Yan W, Liu Z, Yang W, Wu G
Received 27 June 2018
Accepted for publication 18 September 2018
Published 8 November 2018 Volume 2018:10 Pages 5479—5490
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S178261
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background and
aims: SMAD4, as a tumor suppressive gene in human
colon cancer, inhibits the metastasis of colon adenocarcinoma cells. However,
the molecular mechanisms are unclear. miRNAs play an important role in the
pathogenesis and progression of cancer.
Methods: In this study, a deep sequencing technique was used to screen
Smad4-regulated miRNAs in human colon cancer SW620 cell line. Using a
next-generation small RNA sequencing approach, we compared the miRNA expression
profiles of SW620 colon cancer cells transfected with smad4 lentiviral vector
with those transfected with control vector. Six samples were selected and
sequenced randomly each from control group (smad4-negative cell) and Smad4
group (Smad4-positive cells). Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR)
and Western blot (WB) was used to validate the results of sequencing.
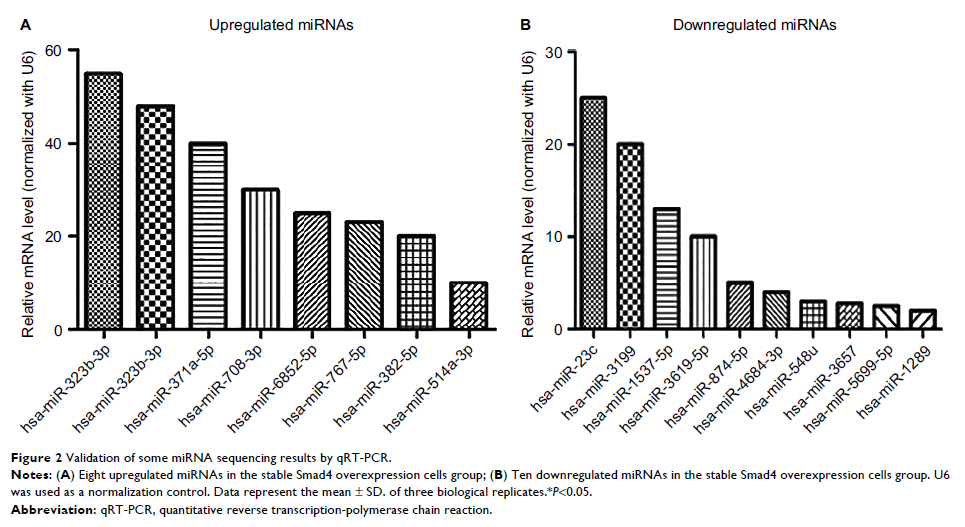
Results: Smad4 reexpression significantly upregulated 43 known miRNAs and
downregulated 10 known miRNAs expression. Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia
of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis of predicted miRNAs targets showed that
these genes were mainly involved in protein-binding transcription factor
activity, vascular smooth muscle contraction, pathways in cancer metastasis,
and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase–Akt signal pathway. qRT-PCR and WB validated
the partial results of sequencing. Reexpression of Smad4 inhibited colon cancer
cell migration and invasion. Smad4 reexpression increased the expression of
E-cadherin (E-cad) and decreased the Vimentin (Vim) and Matrix
Metalloproteinase-9 expression. Restoration of SMAD4 results in a marked
decrease of Vim by inhibiting p-AKT and p-EPHA2, but significantly increased
the E-cad by AKT–EPHA2 pathways.
Conclusion: Smad4 inhibits the migration and invasion ability of colon cancer
cells in vitro and this is the first report of Smad4-mediated miRNA expression
profiling in Smad4-positive and Smad4-negative SW620 human colon cancer cells,
which may help us better understand the role of Smad4 in inhibiting the
metastasis of colon cancer cells and its possible molecular mechanisms.
Keywords: Smad4, miRNA, colon cancer, next-generation sequencing