108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

用于体内 CT/MRI 引导下光热癌症治疗的氮氧自由基修饰的金纳米棒
Authors Xia L, Zhang C, Li M, Wang K, Wang Y, Xu P, Hu Y
Received 20 April 2018
Accepted for publication 2 July 2018
Published 6 November 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 7123—7134
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S171804
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Purpose: This article presents a report of the synthesis, characterization,
and biomedical application of nitroxide-radicals–modified gold nanorods
(Au-TEMPO NRs) for imaging-guided photothermal cancer therapy.
Patients and
methods: Au nanorods were synthesized through
seed-mediated growth method, 4-Amino-TEMPO was added and the reaction proceeded
under magnetic stirring.
Results: With a mean length of 39.2 nm and an average aspect ratio of
approximately 3.85, Au-TEMPO NRs showed good photothermal ability when they
were irradiated by 808-nm laser. Au-TEMPO NRs could be stored in PBS for more
than 1 month, showed no cytotoxicity against both tumor and normal cells at a
concentration of up to 3 mg/mL, and functioned as a dual-mode contrast agent
for CT/magnetic resonance (MR) imaging in vitro and in vivo, due to their high
X-ray attenuation of Au and good r1 relaxivity of nitroxide radicals. Further,
they had a long retention time (~4 hours) in the main organs, which enabled a
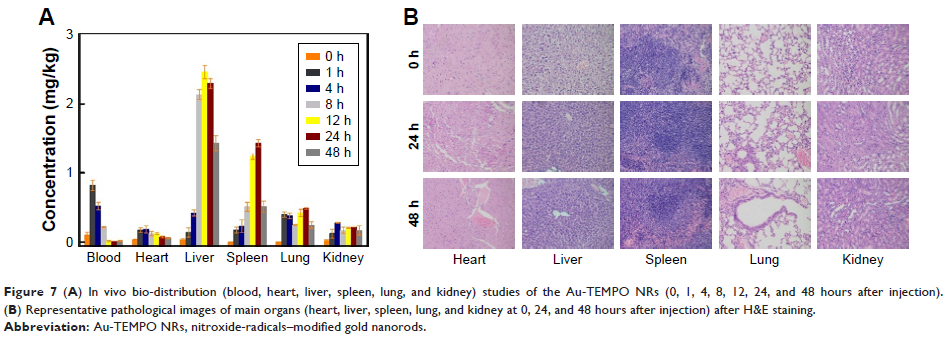
long CT/MR imaging time window for diagnosis. Bio-distribution results revealed
that these Au-TEMPO NRs passively aggregated in the liver and spleen. After
irradiation by 808-nm laser, Au-TEMPO NRs could ablate the solid tumor in 4T1
tumor-bearing mice, which implied they were a potential theranostic agent for
dual-mode imaging and photothermal cancer therapy.
Conclusion: This type of Au-TEMPO NRs with the abilities of CT/MR imaging and
photothermal therapy, can play an active role in imaging-guided photothermal
cancer therapy.
Keywords: PTT, Au NRs, TEMPO, computed tomography, magnetic resonance
imaging