108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

血管活性肠肽对实验性自身免疫性神经炎大鼠模型的影响及在急性炎症性脱髓鞘性多发性神经病变或格林 - 巴利综合征治疗中的意义
Authors Jiao H, Ren H
Received 25 May 2018
Accepted for publication 3 August 2018
Published 6 November 2018 Volume 2018:12 Pages 3817—3824
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S175331
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Background: Guillain–Barré syndrome is an acute inflammatory demyelinating
polyneuropathy that is characterized histologically by demyelination of
peripheral nerves and nerve roots, infiltrates of T lymphocytes, and an
inflammatory response that includes macrophage infiltrates. The aim of this
study was to evaluate the effects of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) in a
rat model of experimental autoimmune neuritis (EAN).
Methods: Forty male Lewis rats were divided into a control group (N=10), an
EAN group (N=10), an EAN group treated with 15 nmol of VIP (N=10), and an EAN
group treated with 30 nmol of VIP (N=10). The rat model was created by
subcutaneous injection of P2 polypeptide (200 µg P257–81) into the base of the tail. Intraperitoneal injection of VIP was given
on day 7. Rats were weighed and functionally evaluated using an EAN score
(0–10). On day 16, the rats were euthanized. The sciatic nerve was examined
histologically and using immunohistochemistry with antibodies against CD8,
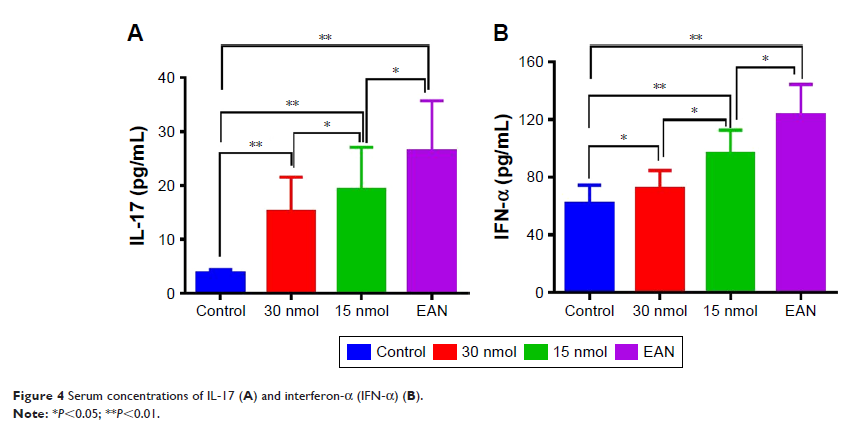
CD68, and forkhead box p3 (Foxp3). Serum concentrations of IL-17 and interferon-α
(IFN-α) were measured by ELISA on day 16 after creating the EAN model.
Results: The VIP-treated EAN groups had increased body weight and improved
EAN scores compared with the untreated EAN group. CD8-positive and
CD68-positive cells were significantly reduced in the EAN group treated with 30
nmol of VIP compared with 15 nmol of VIP. Foxp3-positive cells were
significantly decreased in both EAN groups treated with VIP, and serum
concentrations of IL-17 and IFN-α were significantly lower compared with the untreated
EAN group (P <0.05).
Conclusion: In a rat model of EAN, treatment with VIP resulted in functional
improvement, reduced nerve inflammation, and decreased serum levels of
inflammatory cytokines.
Keywords: Guillain–Barré syndrome, vasoactive intestinal peptide,
experimental autoimmune neuritis, acute inflammatory demyelinating
polyradiculoneuropathy